EASE 5 Third Edition - The modern approach to electro- and room acoustic simulation
Software
EASE represents the established standard in electro- and room acoustic simulation worldwide. The modern platform of EASE 5 combines a highly precise and proven calculation engine with an intuitive user interface and new tools enabling effective workflows adapted to different usage scenarios.
EASE 5 is the ideal solution for acousticians, consultants, specifying engineers, and installation companies to realize their projects efficiently and present them to their clients in a clear and scientifically based manner and from an acoustic professional’s perspective.
Solving Acoustic Challenges

Acousteer world-first real-time simulation engine allowing fast and interactive optimization of sound system coverage and SPL
Intuitive sound system design using advanced aiming functions and extensive signal processing, assessing simulated level distribution, frequency response, and delay times
Easy room-acoustic modeling by tuning absorption and reverberation time and calculating metrics like clarity, speech intelligibility and ISO 3382 parameters
Advanced room-acoustic investigations using reflection analysis, full-length impulse response calculations and auralization
Extensive applicability from immersive designs in entertainment venues and clarity in opera houses to speech intelligibility in airports and SPL coverage in shopping malls
Advancing Your Toolset
Established standard in electro- and room acoustic simulation worldwide supporting a precise simulation engine that matches real-world measurements
Modern user interface and comfortable room editor for efficient workflows, managing simple to complex projects with ease, ranging from initial studies to in-depth evaluations
Large, accurate loudspeaker database including line arrays, steerable columns and matrix loudspeaker systems for almost 300 brands
User-centric feature development with free major updates on a monthly basis
Learning made easy based on introductory videos, extensive support materials and fast technical support
EASE 5 Third Edition
Now available!
Introducing Acousteer
The new real-time simulation engine
Versions & Prices
Starting with EASE
Details
Extension will be at renewal fees
Simulation Software License, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Extension will be at renewal fees.
Simulation Software License, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Extension will be at renewal fees.
Simulation Software License, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Extension will be at renewal fees.
Simulation Software License, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Extension will be at renewal fees.
Simulation Software License incl. AURA and EARS module, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
EASE Renewal & EASE 4 Upgrades
Details
Applies to existing EASE 5 and EASE 4 users.
Simulation Software License, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Applies to existing EASE 5 and EASE 4 users.
Simulation Software License, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Applies to existing EASE 5 and EASE 4 users.
Simulation Software License, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Applies to existing EASE 5 and EASE 4 users.
Simulation Software License, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Applies to existing EASE 5 and EASE 4 users.
Simulation Software License incl. AURA and EARS module, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Details
Applies to existing EASE 5 and EASE 4 users.
Simulation Software License incl. AURA and EARS module, 1 User
The End User License Agreement for EASE 5 applies.
Features
- Importing drawings and 3D models
-
DWG import
EASE 5 allows importing 3D models, or 2D parts of the room, in DWG format. These can be complete rooms or just the basis for drawing a room in EASE.
- Import DWG files from CAD tools such as AutoDesk AutoCAD software, Trimble SketchUp Pro or Rhinoceros 3D by Robert McNeel & Associates
- Supports 3D Polylines, 3D Faces, Polyface Meshes and SubD Meshes
- Supports 2D Polylines, LW Polylines, Arcs, Circles, and Ellipses
- Supports importing of layers or tags for project organization, acoustic material, creation of audience areas and reflectors or parapets
- Ensure model consistency using geometrical analysis tools of EASE 5
- Insert faces in holes and invert wrongly oriented faces to establish a model suitable for acoustic simulation
- Assign acoustic materials to surfaces and add loudspeakers, audience areas as well as receivers to the model
Image
Modeling based on drawings
For many projects, only section plans are available for 3D room modeling. In EASE 5, floor plans, front and section views can be loaded as graphics files and used as a reference for drawing the room model.
- Load various image file formats, such as JPG or PNG
- Adjust orientation according to section plane
- Scale drawings based on known dimensions
- Label drawings and toggle their visibility using the drawings table
- Position drawings in the 3D coordinate system as a reference for entering the room coordinates
- Use projection functions and constraints to derive coordinates from the drawings interactively while entering surfaces, placing loudspeakers, and defining receivers
Image
Import and export of EASE 4 projects (.frd file format)
EASE 5 allows importing and exporting EASE 4 project files in FRD format. This makes it easier to get started in EASE 5 by loading existing projects created in EASE 4.4, as well as exchanging EASE data with 3rd parties who are still using EASE 4.4. Since the two software tools are conceptionally different, there are some limitations with respect to the compatibility between them.
Importing projects from EASE 4.4:
- Faces, loudspeakers, audience areas and listener seats can be imported, objects are not yet supported
- Coated and two-fold faces are converted automatically to EASE 5 faces
- SPK speaker models are not supported and some loudspeaker filters settings are not maintained
- Import log shows all corrections
Exporting projects to EASE 4.4:
- Faces, loudspeakers, audience areas and listener seats can be exported, section drawings are ignored
- Face in faces and holes are converted to EASE 4 faces
- Filters of loudspeakers and processing blocks are combined and exported
- Audience areas with more than four points are split
- Selection sets are exported as objects
Image
DWG export
- Room geometry, material assignments and loudspeakers can be export as CAD model in DWG format
- Faces are exported as polyface meshes
- Materials are converted to layers and respective faces are assigned to the corresponding layer.
- Loudspeaker case drawings are converted to polylines and grouped and named by loudspeaker. These elements are stored in a separate layer.
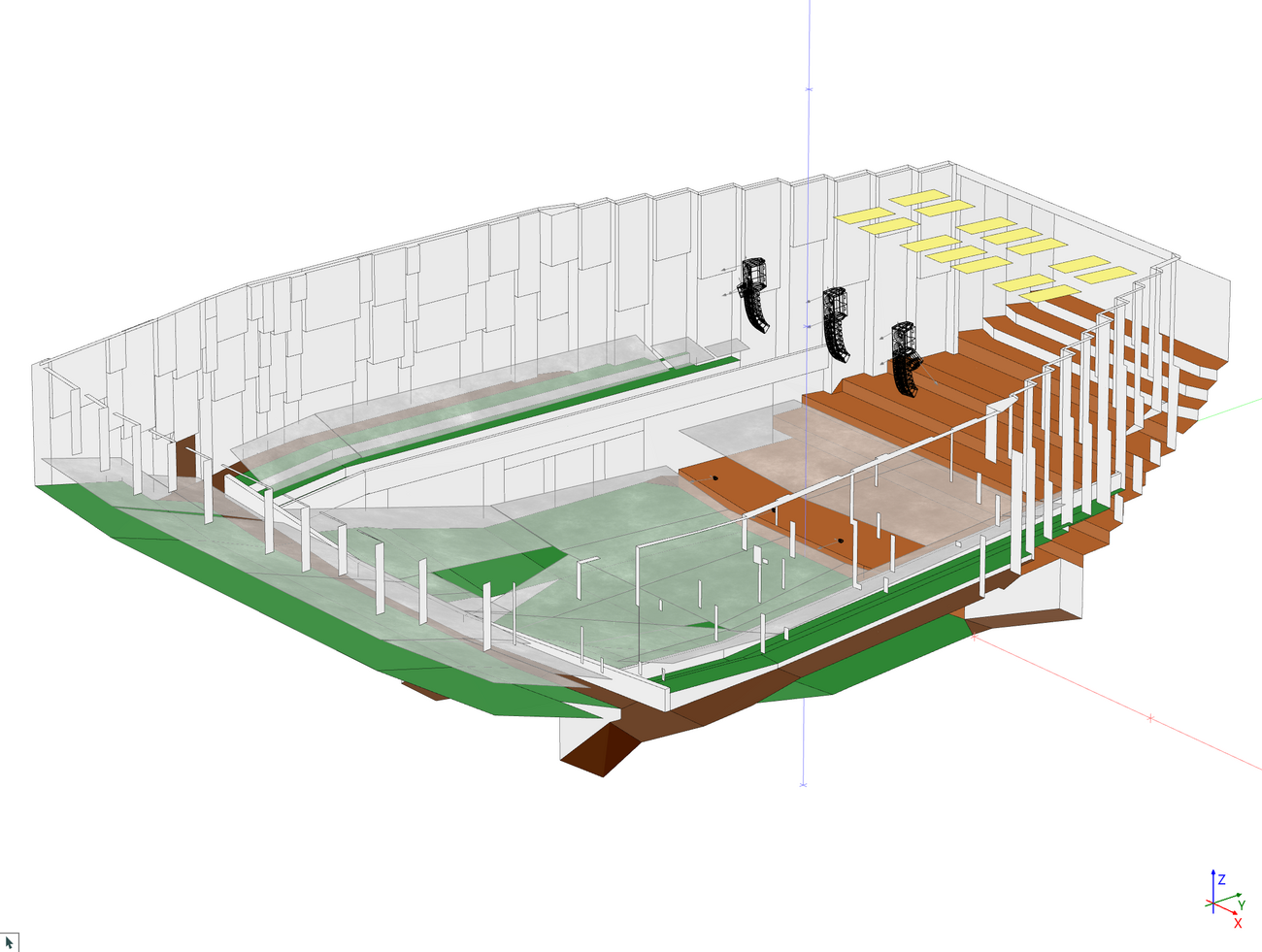
- Creating the 3D model
-
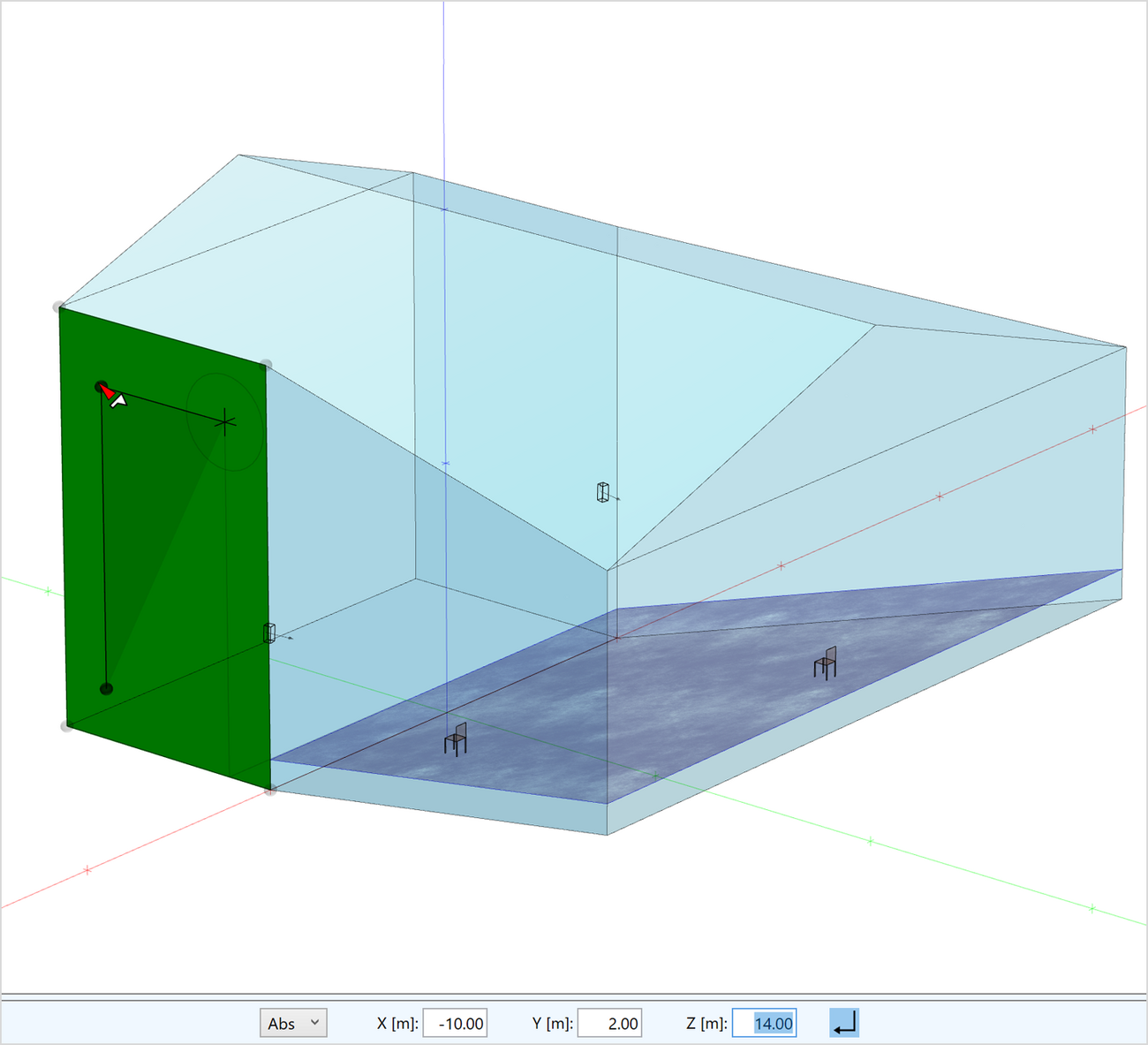
To enter 3D models from the scratch or based on drawings, EASE 5 provides a light-weight CAD editor. The editor allows precise entering of coordinates by an intuitive drawing toolset.
Faces can be created using a range of tools:
- Insert points directly by mouse click or by snapping to existing points
- Insert points by entering coordinates in absolute or relative mode
- Use axis and plane constraints to infer 3D coordinates quickly
- Snap to mid-points, surfaces and other elements
- Infer coordinates from section drawings
- Derive intersections with room element
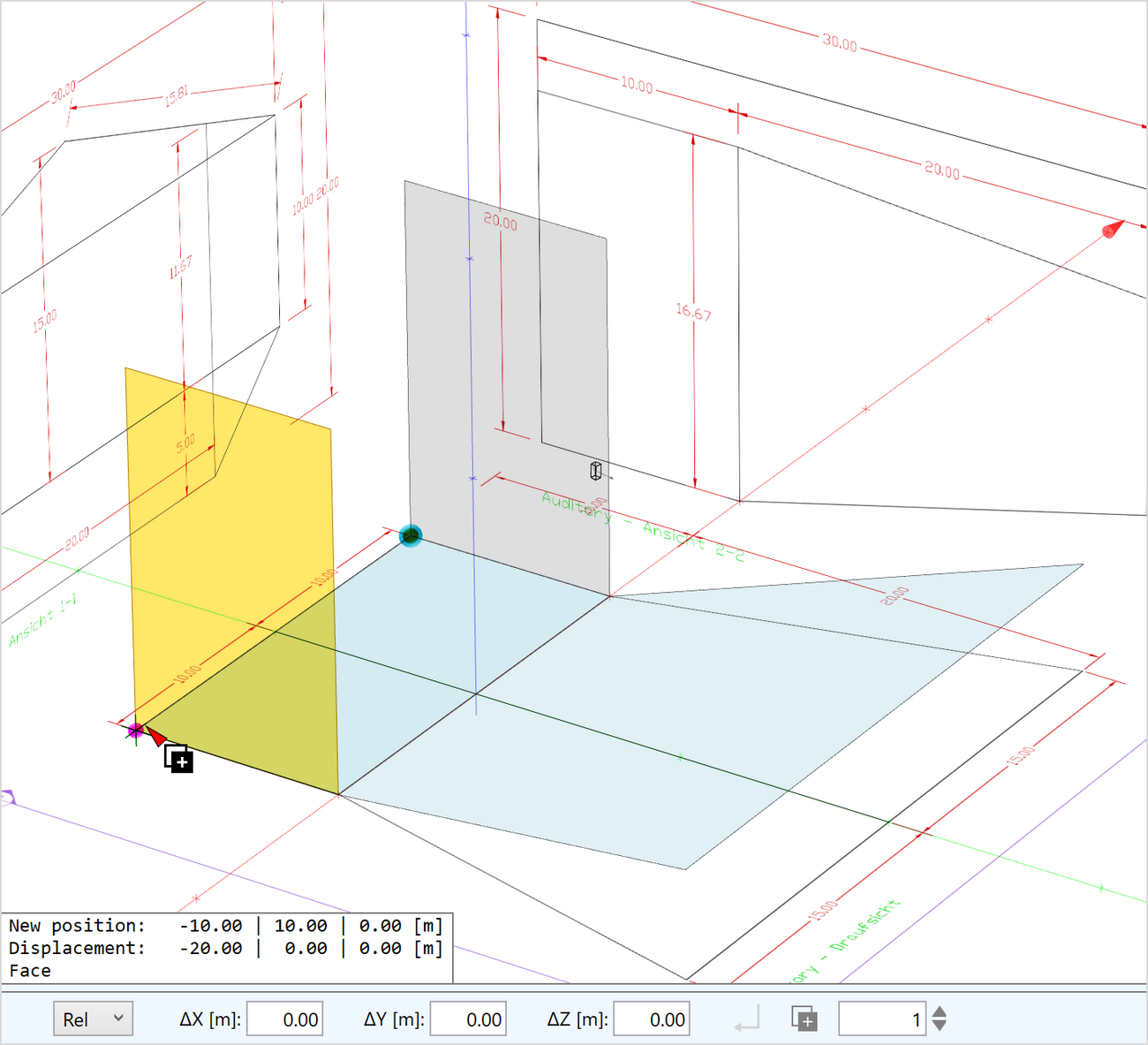
A large set of functions supports the creation and modification of the 3D room model. These functions are consistent with the drawing toolset provided for creating faces and are available for:
- Inserting loudspeakers, audience areas, listener seats
- Inserting faces in faces
- Inserting circles and arcs
- Moving room elements to a new location
- Extruding faces to create rooms or 3D bodies
- Duplicating room elements one or multiple times
- Rotating parts of the room or the room as a whole
- Choosing an anchor point anywhere in the model for move, duplicate, rotate and extrude functions
- Moving vertices and points
- Adding or combining projects in EASE format or DWG format
Additional functions supporting the room-building process include:
- Multi-selection - selecting and modifying multiple items at once
- Mirror items in X- and Y-direction
- Joining and subtracting surfaces
- Create two-sided face configurations
- Invert the orientation of faces
- Insert audience areas above faces
- Status display with context information about the selected element
- Measurement of distances and delays
- Previews during editing steps
- Full undo / redo functionality
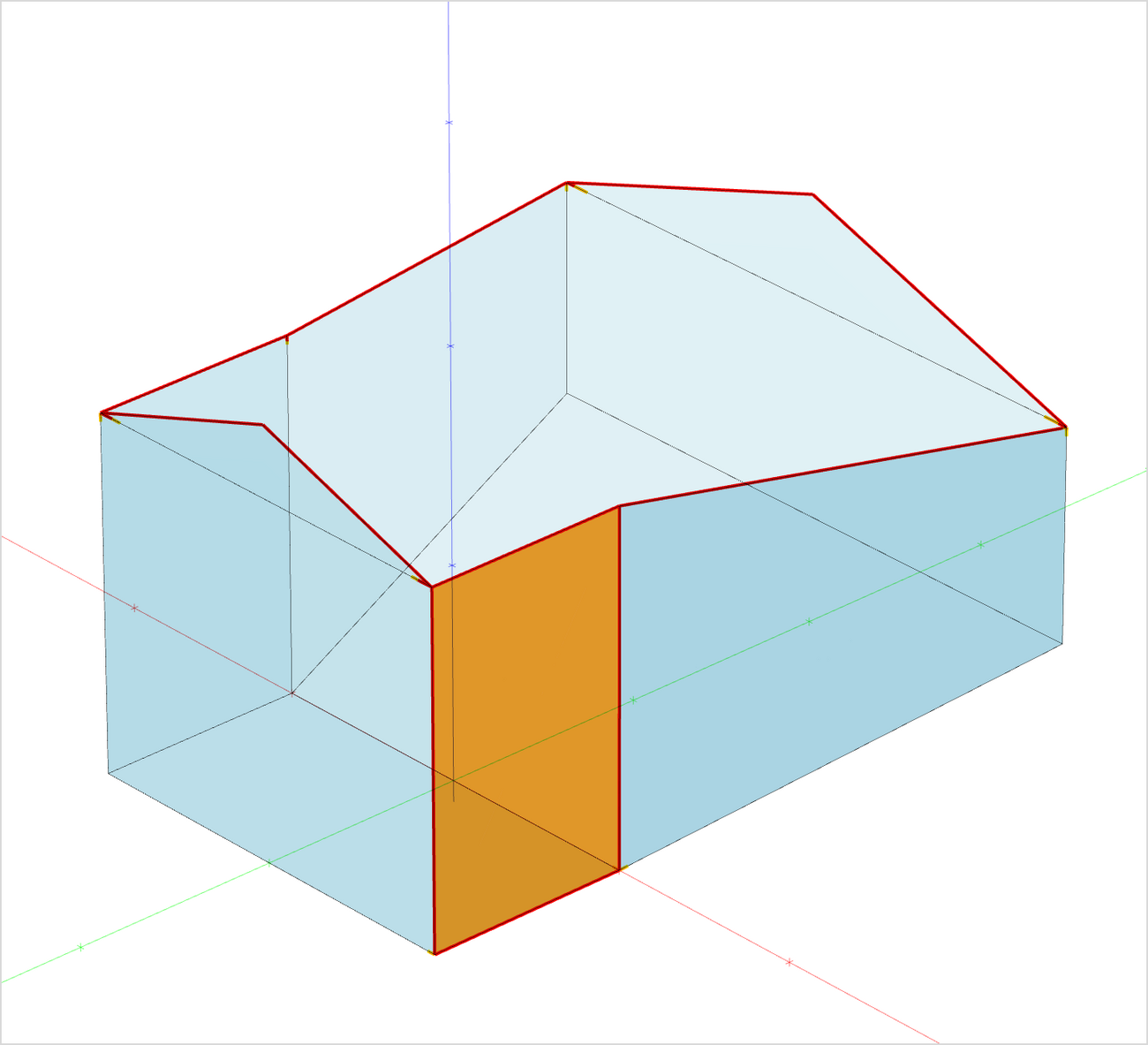
When it comes to finetuning the model, preparing it for the simulation and fixing potential errors, several tools and views help to find potential geometrical problems in the model or acoustically wrong oriented faces.
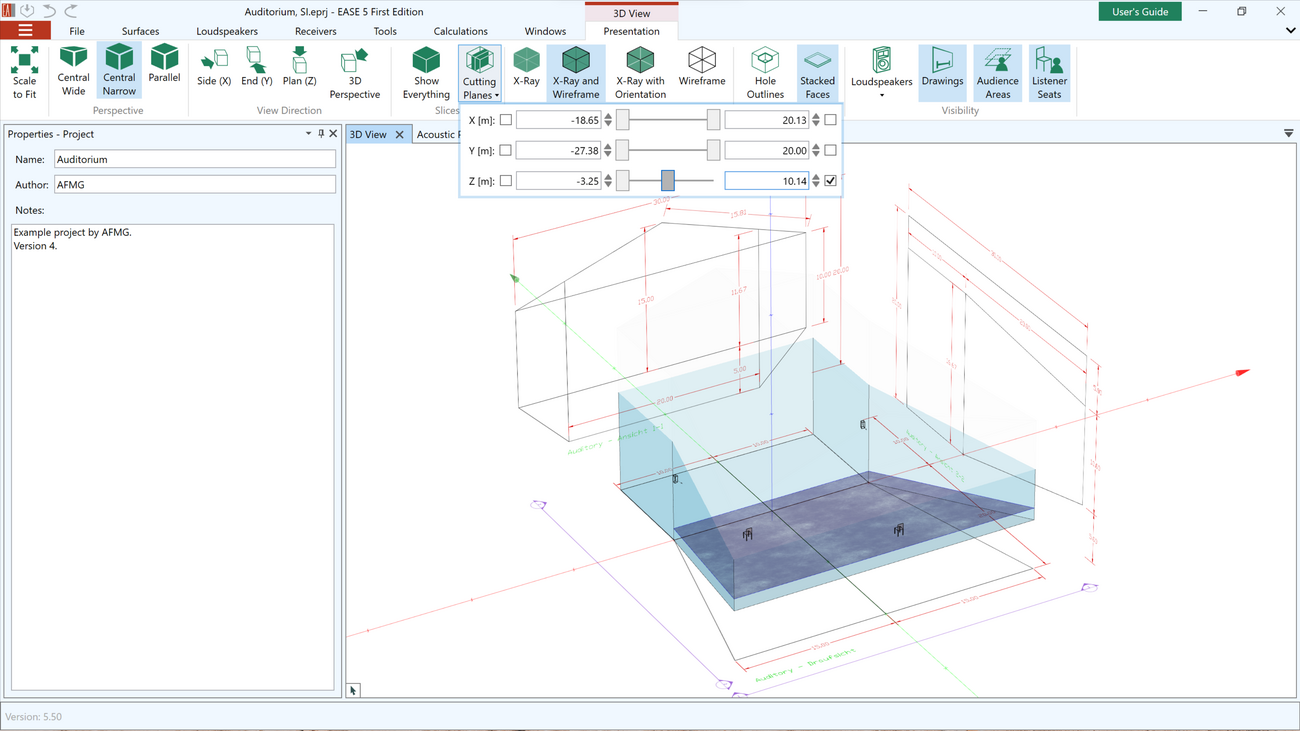
- Apply view slices to hide parts of the model
- Use the x-ray and wireframe views to better understand the 3D structure of the model
- Switch to parallel perspective to verify model consistency using standard view directions
- Activate geometrical analysis tools that highlights holes and stacked faces in the model
- Refer to the calculation results for room volume and surface areas
For detailed information, please have a look at the hands-on video tutorial Building a room model based on 2D drawings in EASE 5:
- Clear software structure and environment
-
Window management
EASE 5 is structured in a clear and flexible way. The room model, the associated data as well as the results can be accessed in different windows. The software is subdivided into a main program and the calculation modules. The main program offers the following windows:
- One or multiple 3D views for viewing and editing the room model in 3D
- Properties window for selected items
- Configurator window for advanced loudspeaker systems
- Materials in Use window for managing wall materials
- Loudspeakers table
- Filters window
- Processing blocks window for managing signal processing of loudspeaker groups
- Acoustic parameters window
All windows of the main program can be resized, moved, undocked and docked. The window layout is remembered automatically.
The calculation modules are linked to the main program and have each their own main window. These modules are:
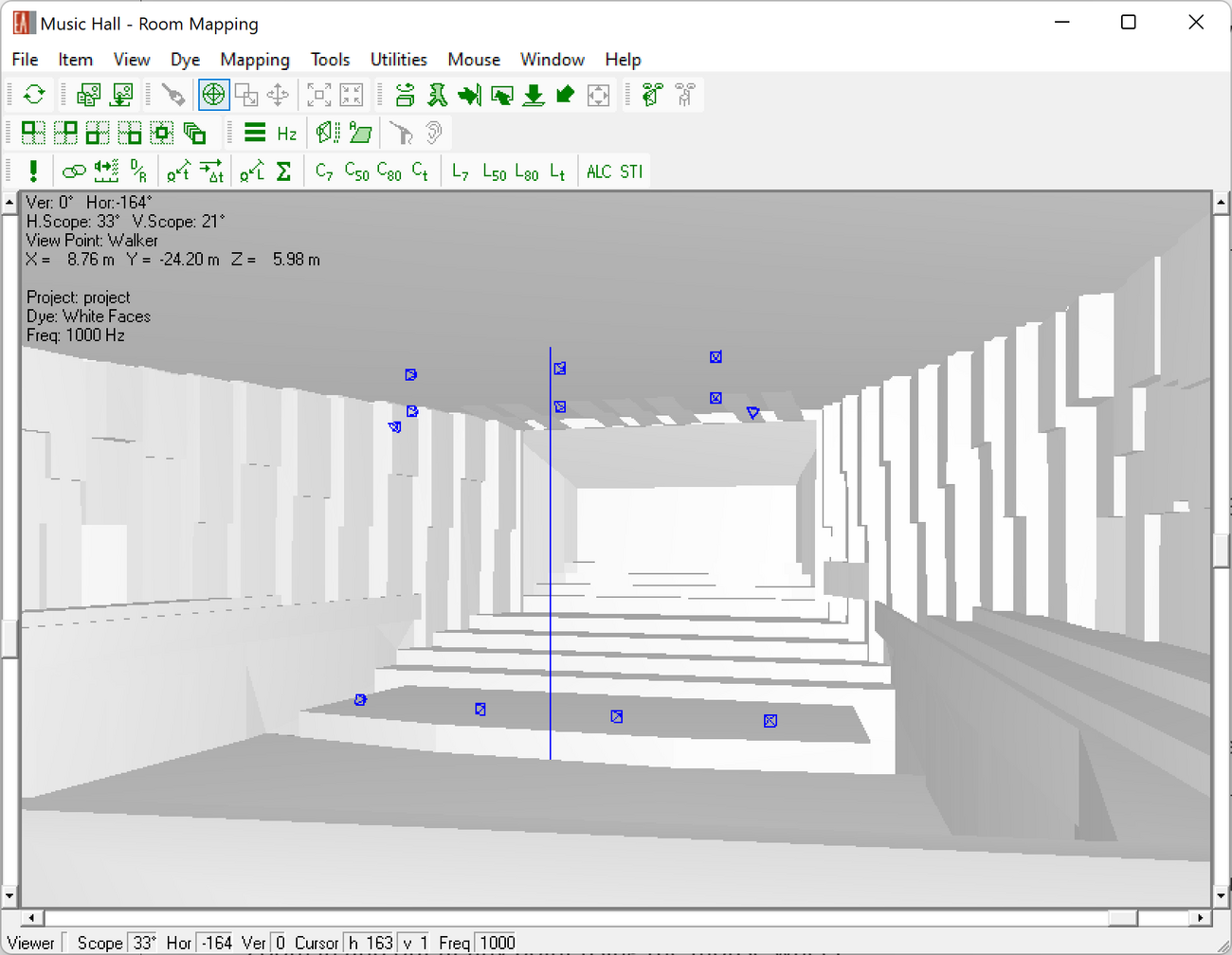
- Room Mapping for viewing the room, calculating mappings and reflectograms
- Ray Tracing for generating reflectograms and response files
- Probe for analyzing and post-processing reflectograms and response files
- EARS for auralizing response files
Additionally, the material editor is available as a module controlled by the main program.
Views
The following presentation views and view settings are available for the 3D model:
- Coordinate system indicated by axes
- Central perspective – narrow and wide view angles
- Parallel perspective with X, Y, Z and 3D standard view directions
- Slices in X, Y, and Z planes can be used to hide parts of the model
- The X-Ray, X-Ray and Wireframe, Wireframe modes allow better understanding of the 3D structure of the room
- The X-Ray with Orientation mode shows the inside/outside orientation of the surface elements
- The Solid rendering modes provide different ways to visualize the room model based on default colors or material colors.
- Highlight holes and stacked faces using the Geometry Analysis modes
- Look from loudspeaker or listener seats
- Loudspeakers can be displayed as symbols or using their cabinet drawings
- Faces, loudspeakers, section drawings, audience areas and listener seats can be hidden, as a set or individually
Additionally, the Room Mapping module offers different views of the 3D model.
Navigation
Using the mouse as well as keyboard functions the model can be viewed and navigated according to standard conventions.
- Zoom in and out at any point using the mouse wheel
- Pan the model
- Rotate the model in any direction
- Scale-to-fit functions for full view and for zoom on selected room elements
- Status text shows mouse location and view angles
- Right mouse menu for context functions
Please see the related FAQ in addition.
Saving Graphics
The content of each window can be copied to the clipboard for further use in other software. It can also be saved as a graphics file.
- Extensive loudspeaker database
-
Largest database of sound Sources, in GLL format
With EASE you can perform simulations supported by an extensive loudspeaker database including around 3000 data sets from about 300 brands, covering the majority of the world’s renowned loudspeaker manufacturers. Highly accurate loudspeaker data is stored in the GLL format and allows simulation accuracy of up to 1 dB.
Additionally, AFMG provides a number of generic loudspeaker models including a line array, several ceiling loudspeakers, a two-way loudspeaker and an omnidirectional source.
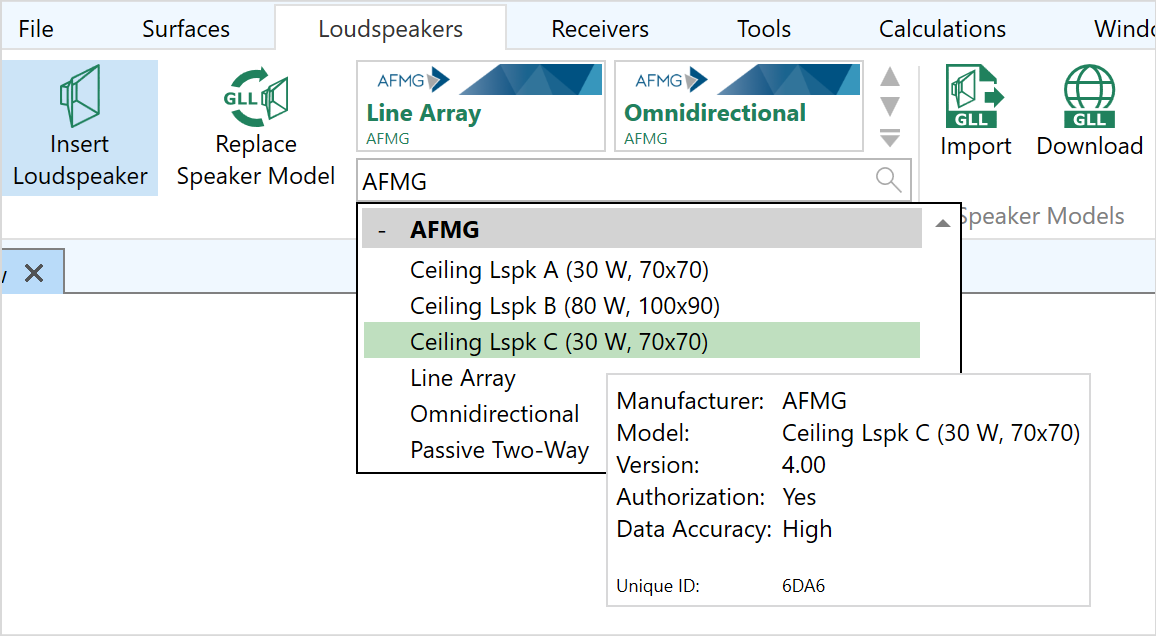
Managing the database
For EASE 5 the loudspeaker databases, sorted by brands, can be downloaded from the AFMG website and then imported via the ribbon menu.
The following functions are available for viewing and selecting from the database
- Filter database by search function
- List of speaker models sorted by brand and data file version number
- Authorization status and data accuracy are indicated
- Logo embedded in speaker model files
- Includes Unique ID for reference
- Supports both GLL- as well as DLL-based speaker models
- Outdated or invalid speaker models can be removed from the database
- Loudspeaker handling
-
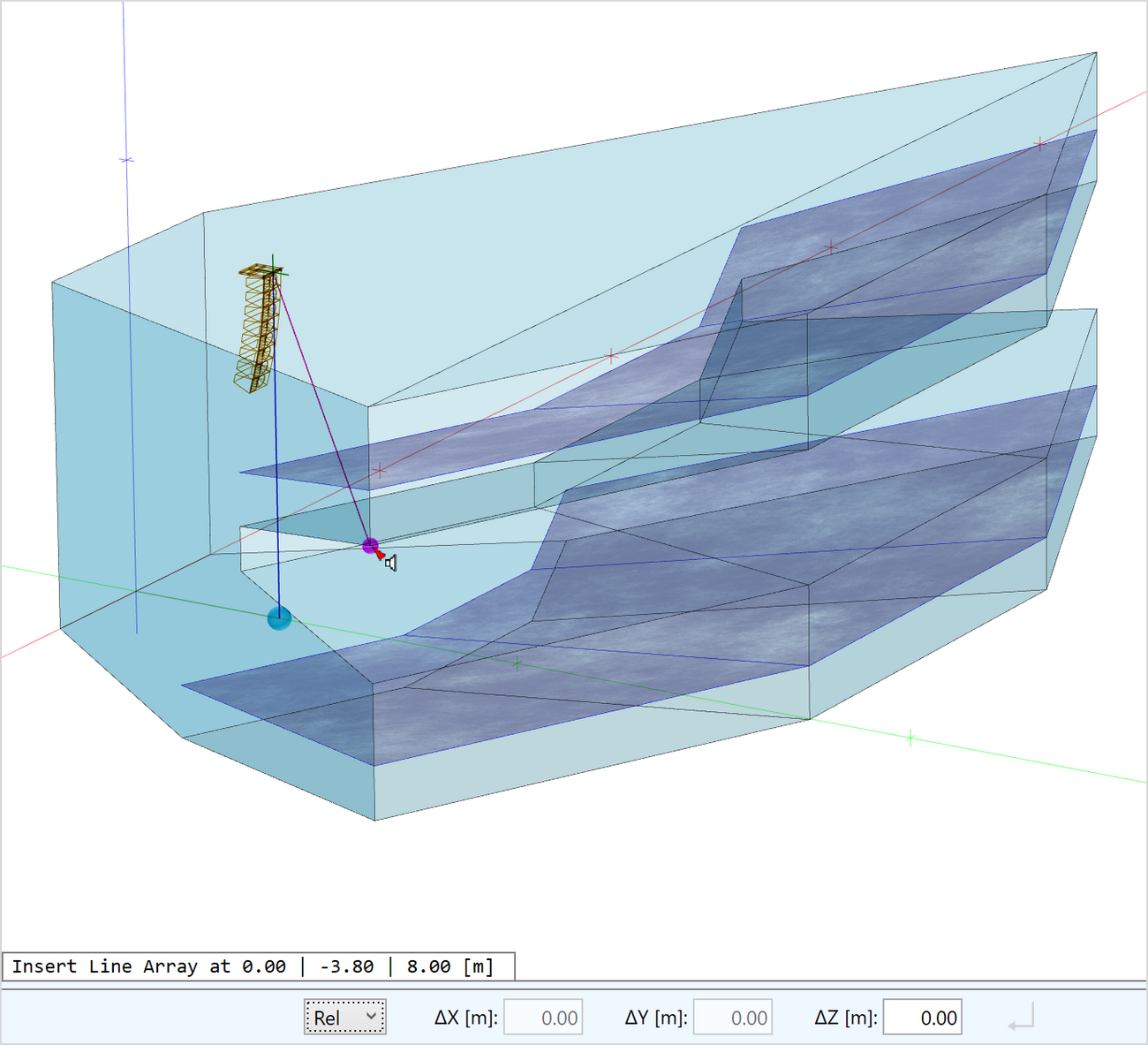
Inserting loudspeakers
Loudspeakers can be inserted into the model by selecting a speaker model from the database or by duplicating loudspeakers that already exist.
- Insert loudspeakers using the drawing toolset of the CAD editor
- Specifically, loudspeakers can also be placed on surfaces and will be automatically oriented in the direction of the surface element
- A preview shows the case drawing of the loudspeaker in advance
- Replace the speaker model by another one using the Replace function
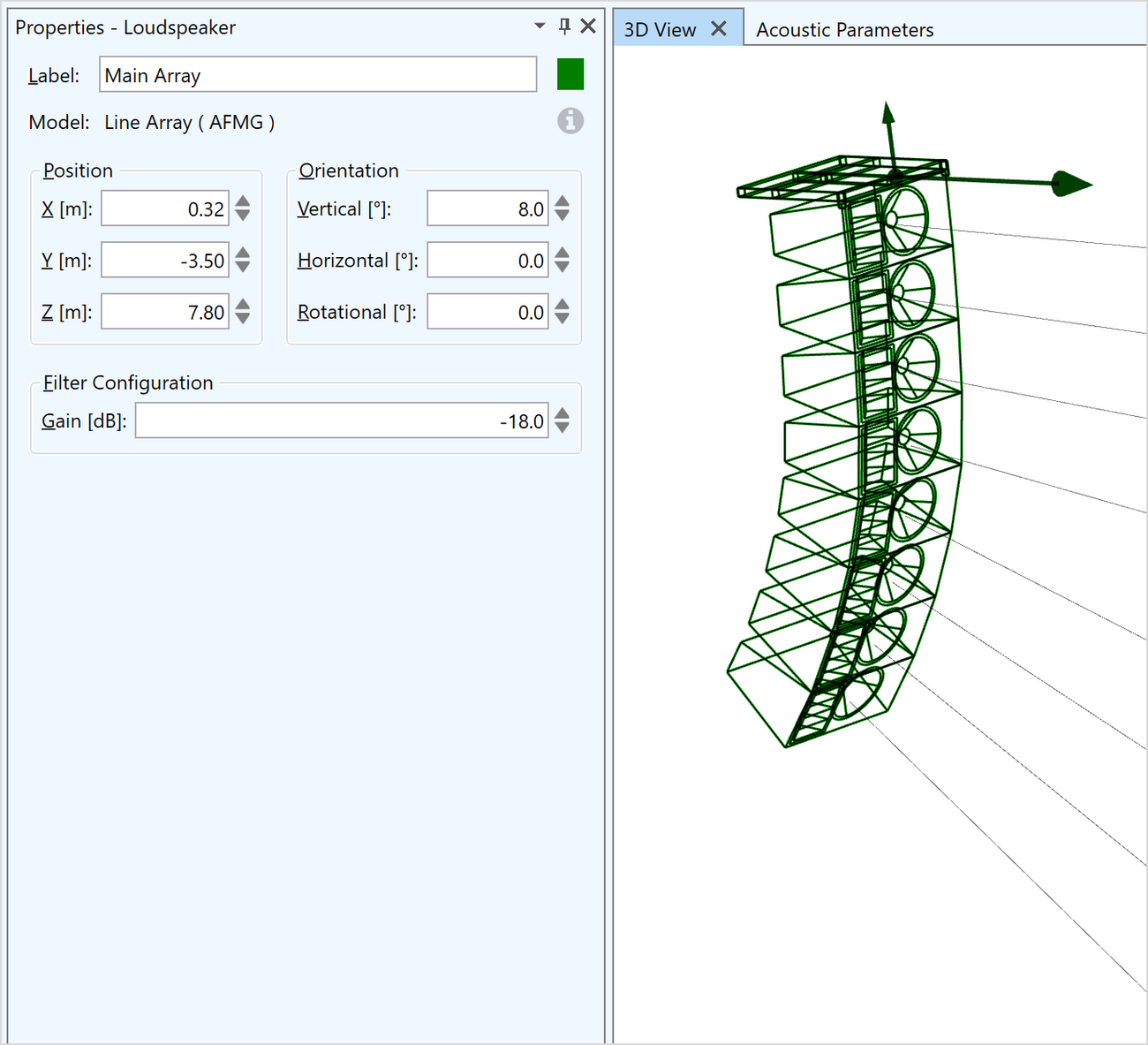
Configuring loudspeakers
The primary properties of a loudspeaker are configured through its properties window.
- User-defined label
- Information only: Speaker model and brand as well as additional information
- Position (X, Y, Z coordinates)
- Orientation (Hor, Ver, Rot angles)
- Gain settings (filter configuration)
Loudspeaker objects are visualized as follows:
- Case drawing or symbol display
- Aiming lines in the 3D views
- Arrows indicating radiation and upward direction
Loudspeaker configurations can also be copied to other loudspeakers. Predefined configurations (presets) can be selected as well.
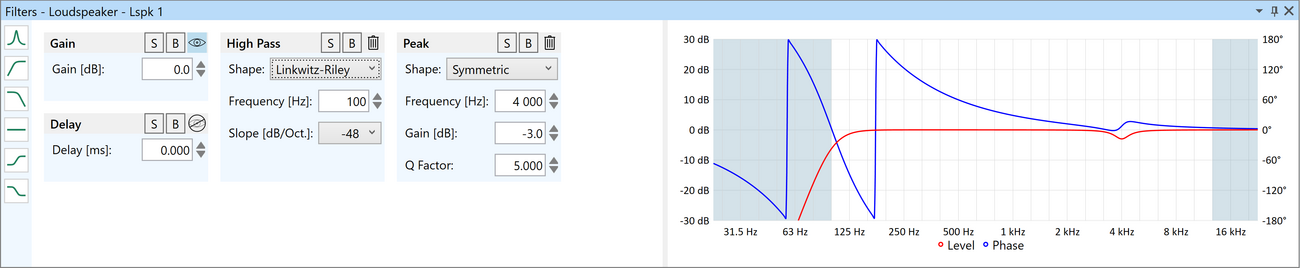
Signal processing for loudspeakers
Signal processing functions can be defined in the Filter Stage window for each loudspeaker as follows:
- Gain and delay
- Add and remove one or several filters:
- High- and low-shelf
- Peak (symmetrical and asymmetrical)
- All-pass
- High- and low-pass (Butterworth, Linkwitz-Riley and Bessel)
- Filter functions can be set to bypass or solo mode
- Graph shows resulting complex filter transfer function
- Additionally, input configurations and predefined filters as provided by the manufacturers can be selected
- Loading beam-steering settings and filter configurations from XGLC configuration files
- Invert polarity, bypass, and reset functions
All filter functions are also available for each input of a loudspeaker or line array element.
Filter settings of all filter stages can be also exported and imported using the XGFB text file format.
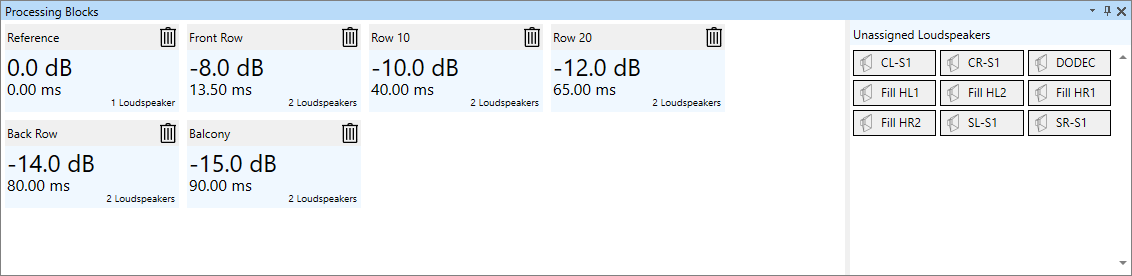
Processing blocks
Processing blocks can be used to group loudspeakers and to assign various signal processing functions similar to individual loudspeakers:
- Add and remove loudspeakers using drag & drop or multi-select
- User-defined label
- Gain, delay, and filter functions via the Filter Stage window
- Attached loudspeakers are automatically highlighted in the 3D view and vice versa
Global EQ
The Global EQ can be used to apply signal processing functions to the whole sound system. Gain, delay, and filter functions are available via the Filter Stage window.
Also, an additional safety margin can be applied to the input signal. If the achievable maximum output SPL of the sound system is a design aspect, this setting can be used to include additional headroom in the simulated signal processing.
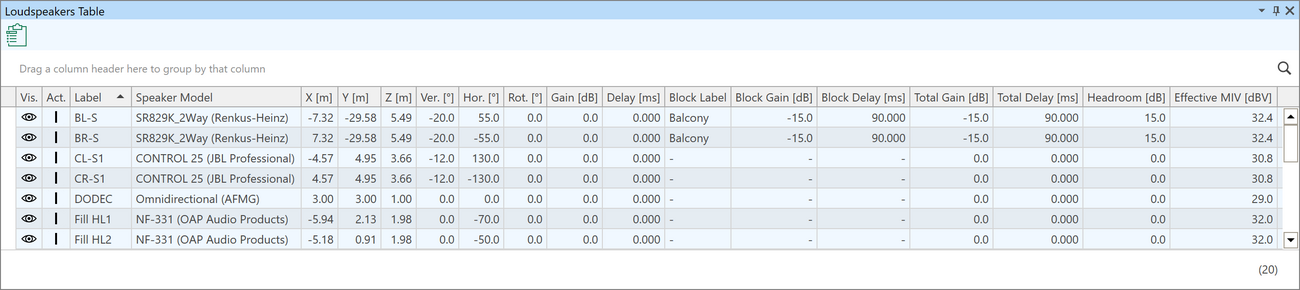
The table can be exported to the clipboard for further use. Loudspeakers can be highlighted and selected in the table.
A sound system configuration in XLD text file format can be loaded as a new project or added to an existing project. The sound system configuration can also be saved in this format for import on other platforms, such as immersive design tools, manufacturer aiming software, or environmental noise prediction. - Configuration of line arrays and clusters
-
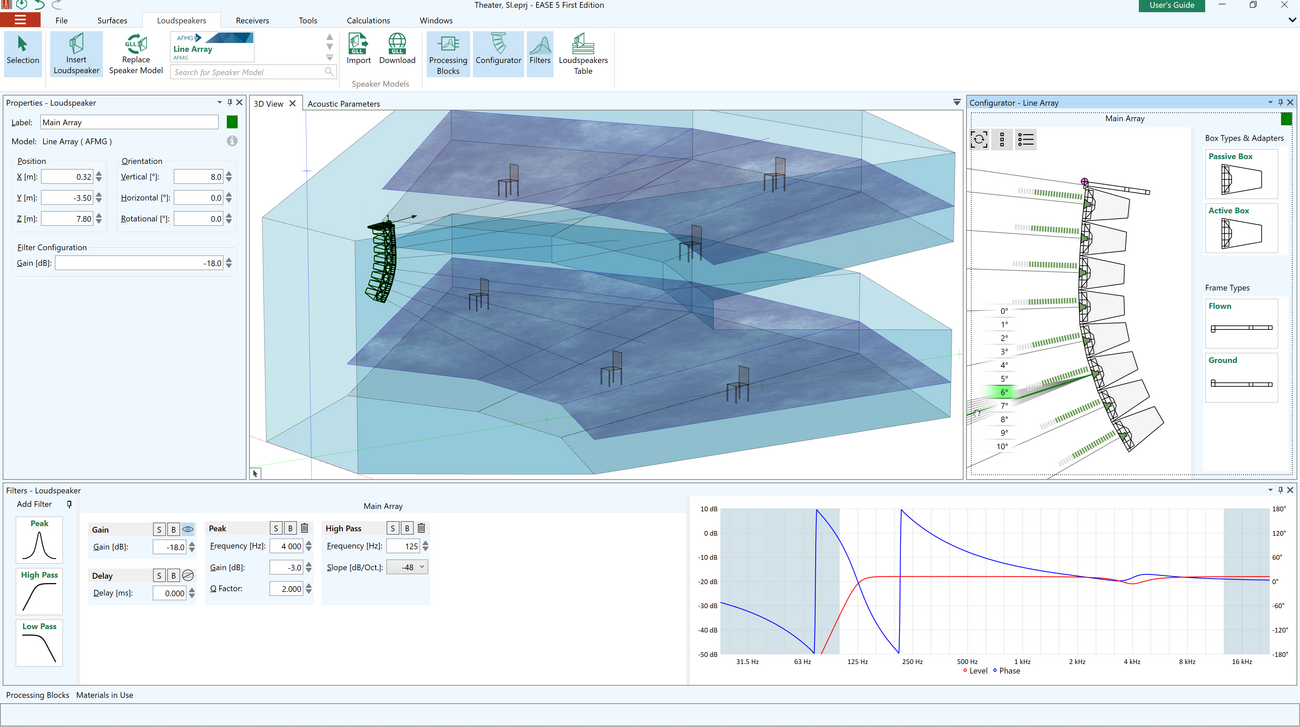
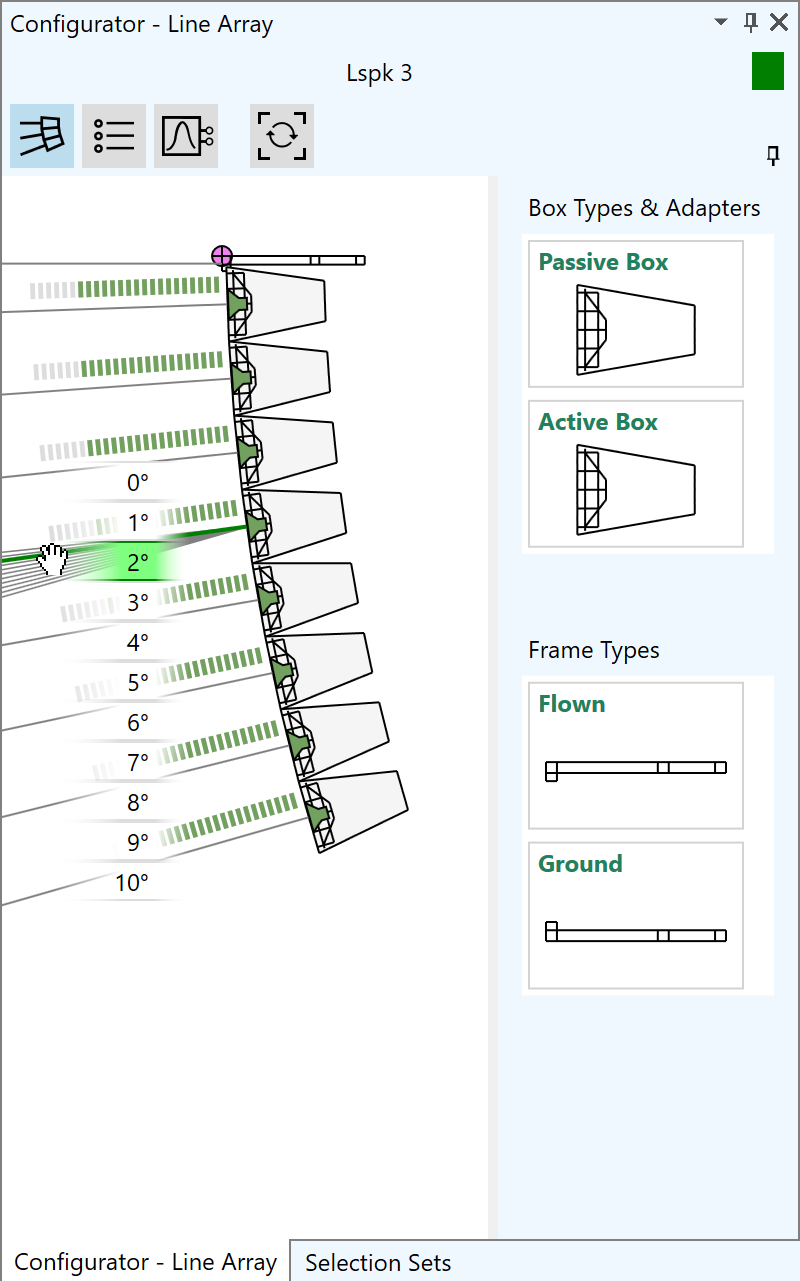
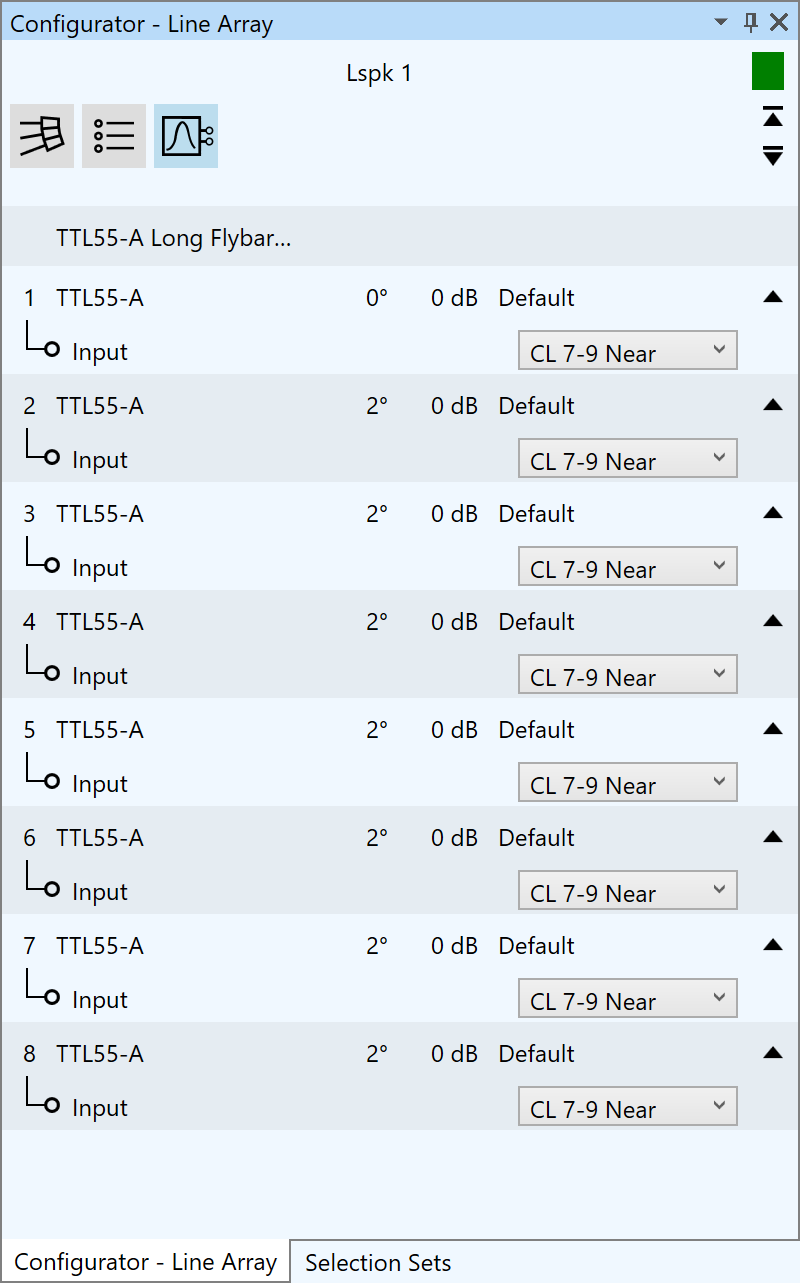
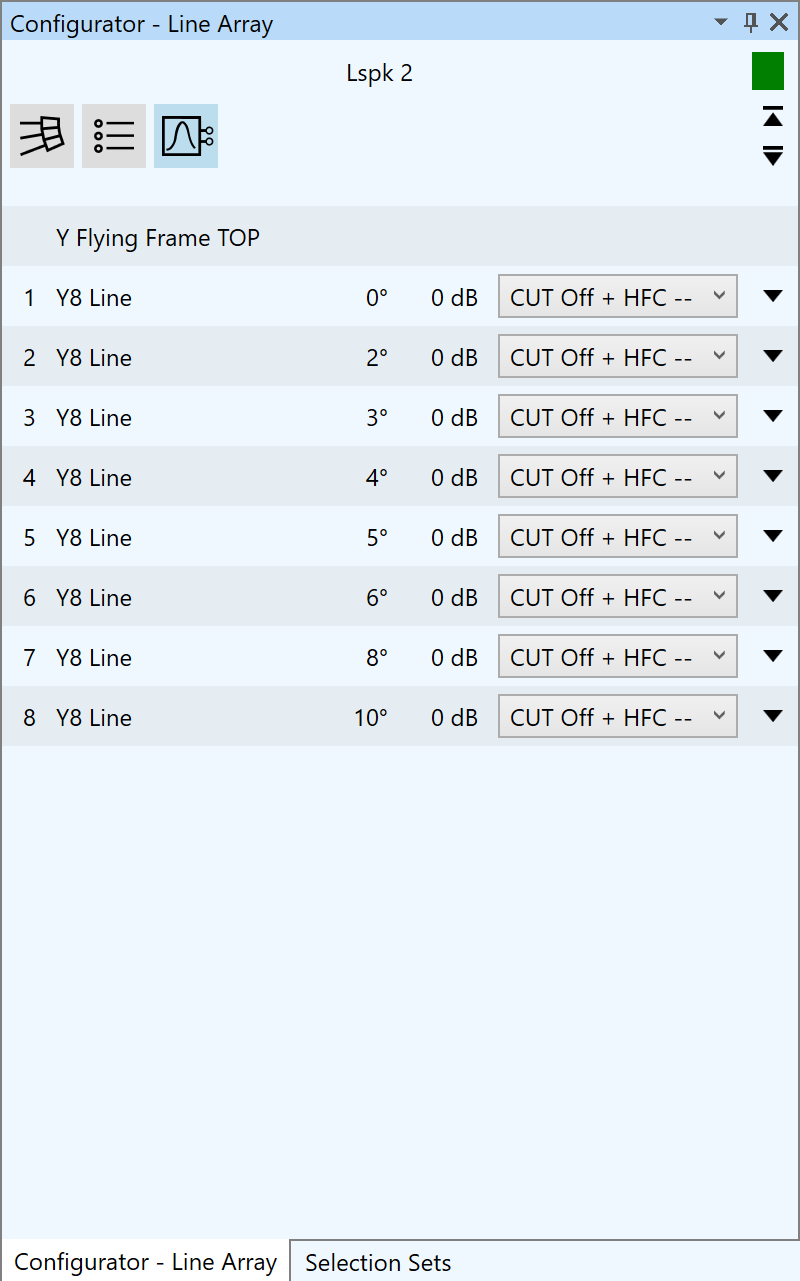
The Configurator window of EASE 5 provides configuration functions for advanced speaker models. In the case of DLL-based proprietary speaker models the embedded dialog window can be accessed through the Configurator window. For GLL-based speaker models, line array systems as well as loudspeaker clusters can be built and modified easily.
For line arrays, the following functions are available:- Select from available frame types, such as flown or ground stack
- Append, insert or remove boxes based on available box types
- Adjust splay angles interactively by drag & drop
- Set gain per array element
- Select input configurations and predefined filters as provided by manufacturer
- Define filter settings for each input of each array element
- Switch between tuning view and schematic view as well as tabular overview
- Indicator shows configuration warnings and errors
- Line arrays are automatically preconfigured using the first preset in the GLL file
- Make use of different settings for optimal workflows
For loudspeaker clusters similar functions are available depending on the definition of the GLL file.
In addition to manual setup, a configuration can be loaded also from an XGLC file. These files can be saved from within another software such as AFMG’s EASE Focus or from EASE itself.
Line array configurations can also be copied to other line arrays.
- Material management
-
Database
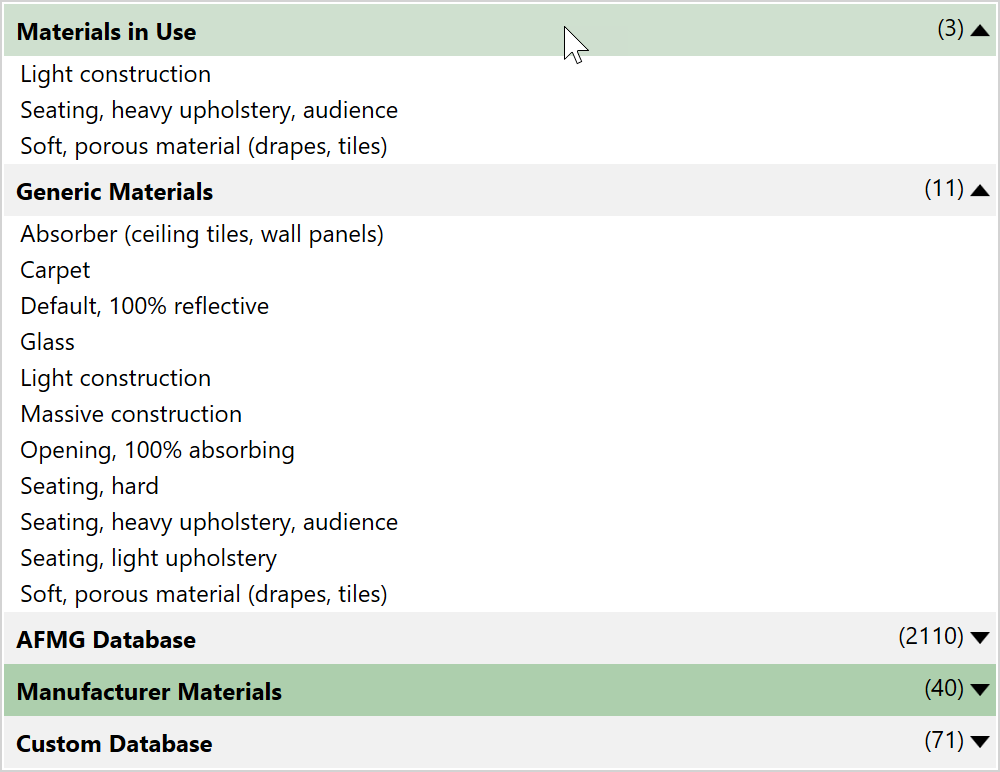
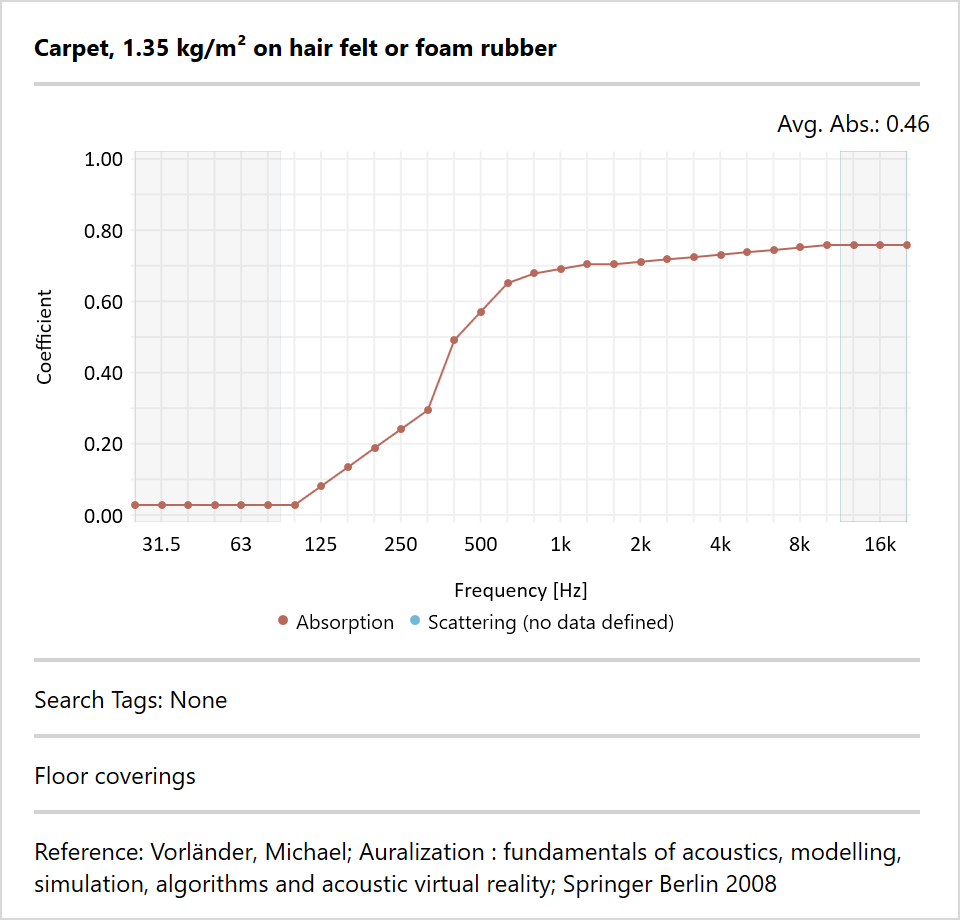
EASE 5 is delivered with an extensive, reviewed database of materials for ceilings, walls, and floors. These materials are assigned to faces in order to determine the acoustic properties of the face.
The database includes a number of categories, namely the materials loaded in the current project, a small generic database designed by AFMG, a large curated database by AFMG, manufacturer database, and a user-defined database with custom materials. The following functions are available for viewing and selecting materials from the entire database:- Filter database by search function
- List of materials sorted by category and name
- Material name and description
- Reference or source of origin
- Curve showing frequency dependent absorption coefficients as well as scattering coefficients
- Average absorption coefficient
- Search tag
- Exporting material as MAT file
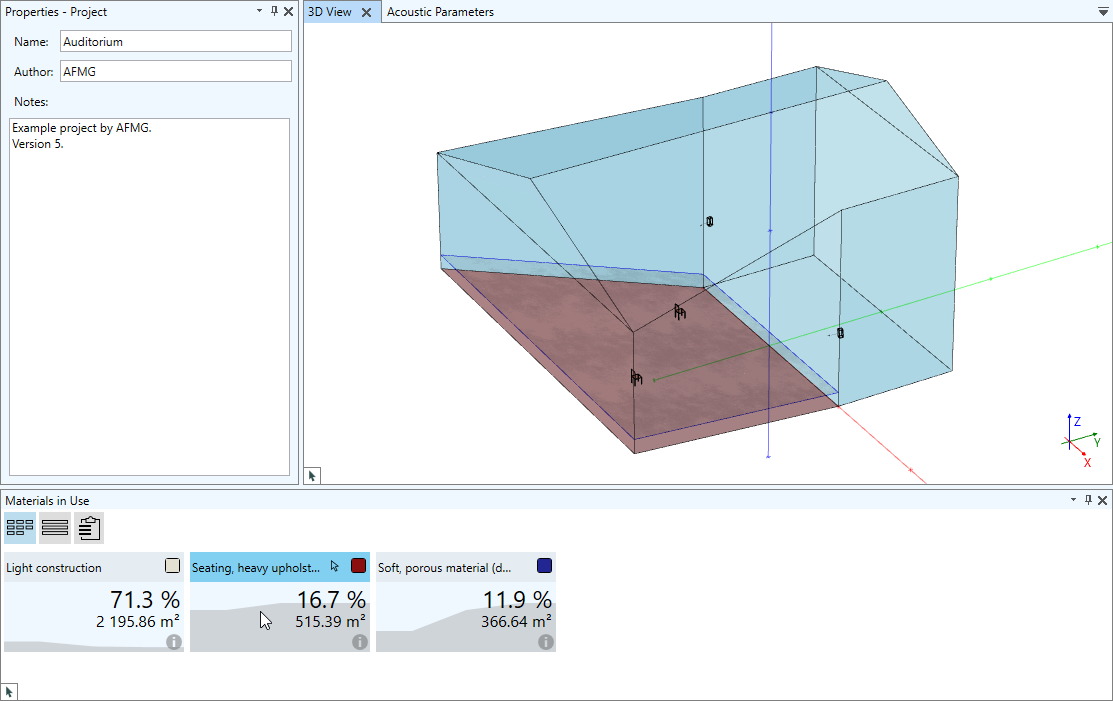
Materials in Use window
All materials used in the project are shown as tiles in the Materials in Use window and provide the following additional information:
- Surface area covered with this material
- Percentage % of the whole surface area covered with the material
- Equivalent absorption area
- Data as available in the database, such as description or absorption curve
The materials in use can be visualized also as a table, which can easily be exported for insertion in reports.
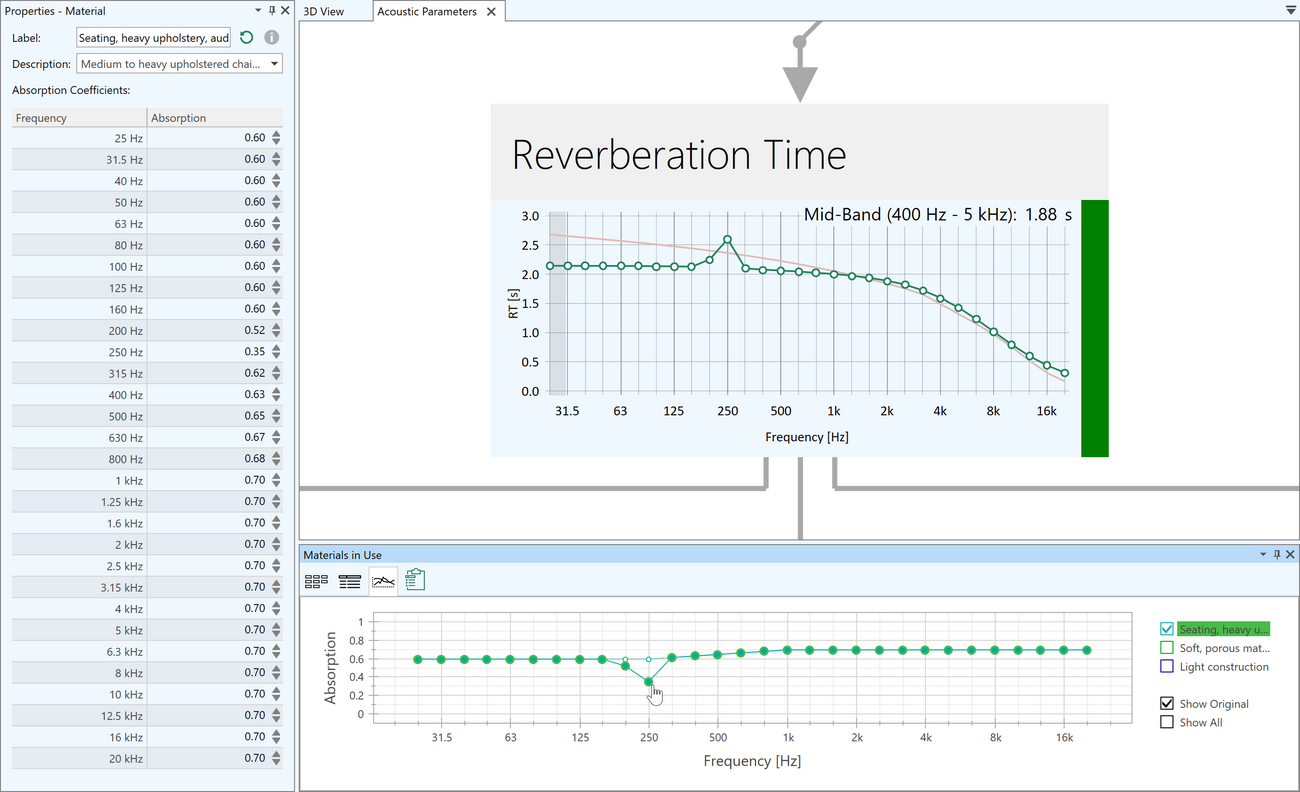
A user-defined color can be assigned to each material used in the project.Viewing and modifying absorption curves
Materials assigned to faces in the project can now be modified very easily in order to calibrate to a measured reverberation time or achieve a target RT.
- Edit label, description, and absorption coefficients in the Material Properties window
- View and modify absorption curves using the graphical editor in Materials in Use window
- Original material and coefficients curve are displayed and remain available as a reference
- Use the combined view with measured and calculated RT for tuning
- Modified materials are stored with the project but can be exported to the local database
Material Editor
In order to create new materials or modify materials of the custom materials database, the material editor can be used to insert or adapt absorption coefficients:
- Modify absorption coefficients of materials used in the project to achieve the measured or desired target RT curve
- Enter or adjust scattering coefficients of project materials
- Define new materials according available measurement data or publications
- Import existing material database from EASE 4.4
- Receivers
-
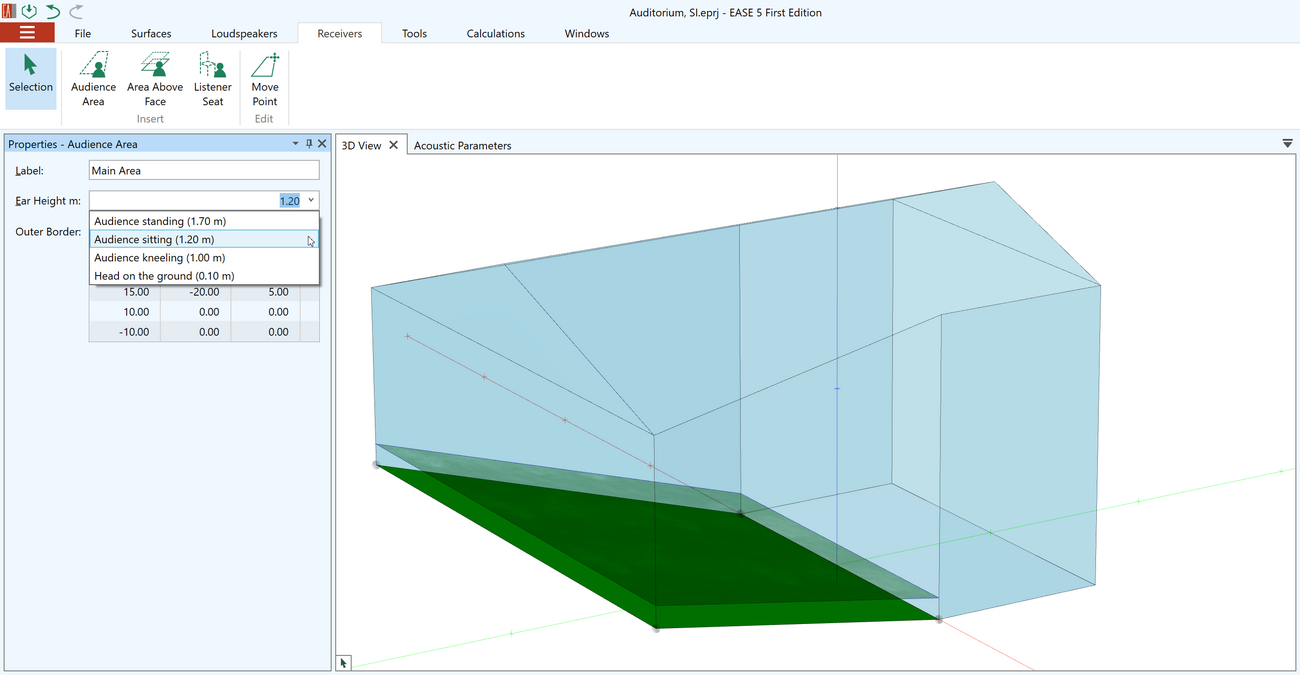
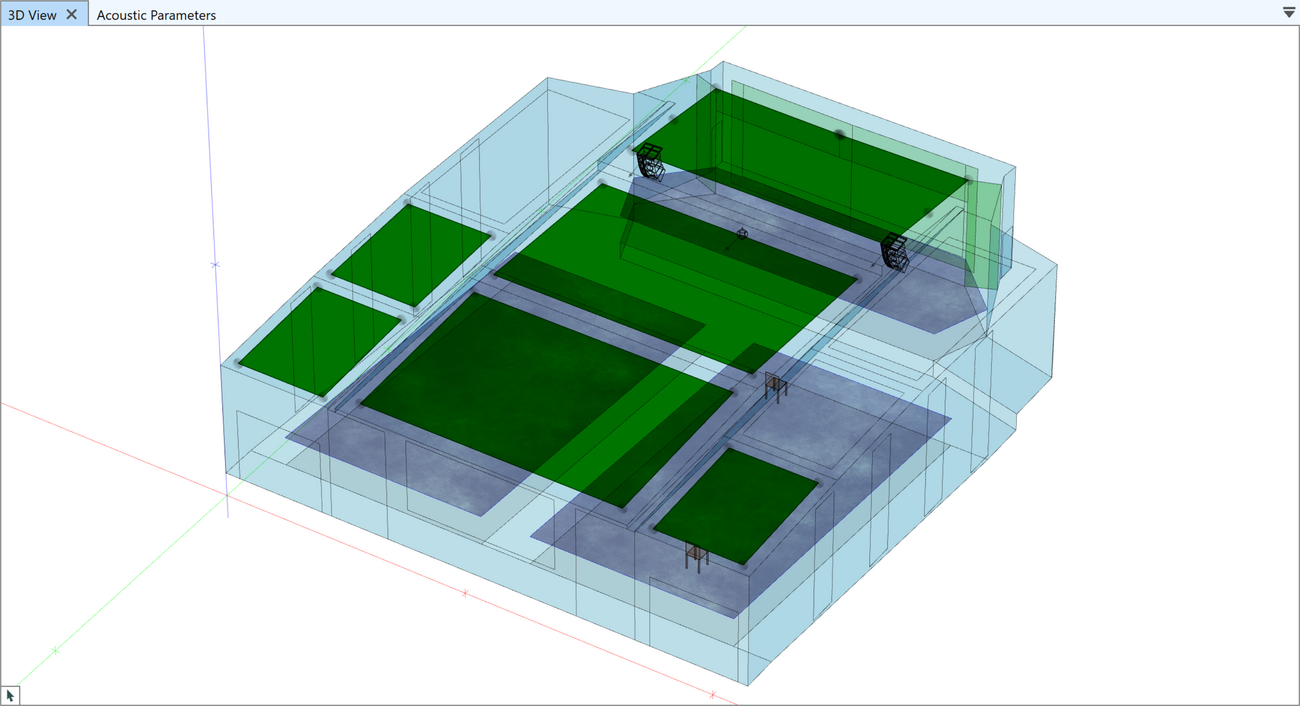
Audience Areas
Audience areas represent the virtual planes that are used for mappings and calculations. Audience areas can be inserted into the model manually using the drawing toolset of the CAD editor. They can also simply be added using the Area Above Face function or by duplicating audience areas that already exist.
Audience areas support the following properties:
- User-defined name
- Ear height setting – for example, for standing or sitting audience
- Arbitrary number of points
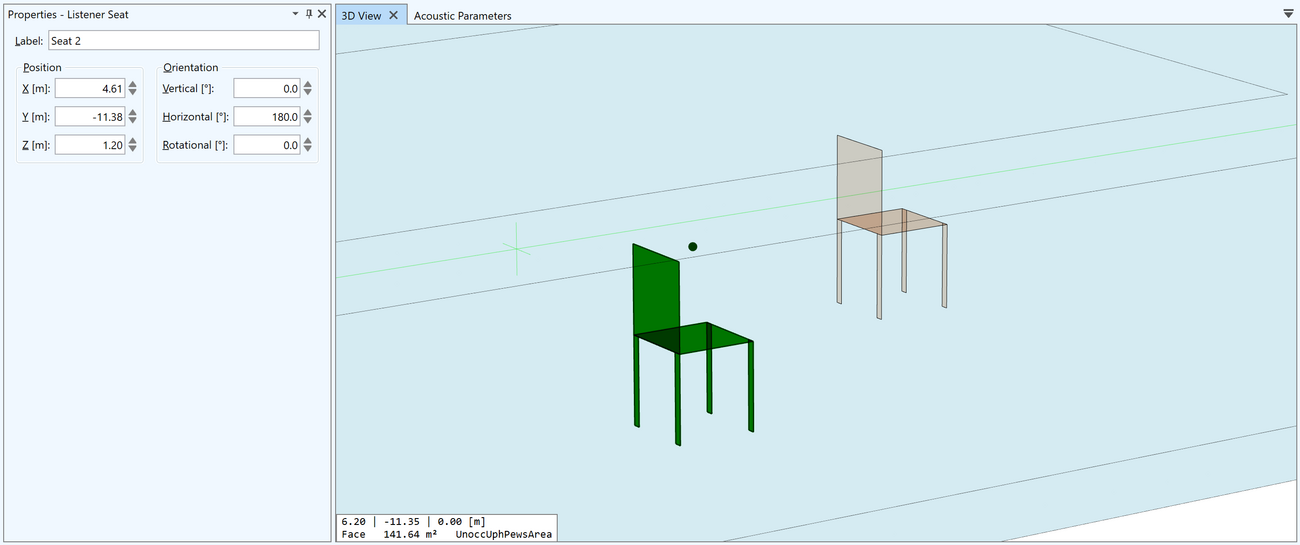
Listener Seats
Listener seats are used to represent important listening positions or measurement positions. Mapping and auralisation results can be calculated at these specific locations.
Listener seats can be manually inserted into the model or by duplicating a listener seat that already exists.
- Insert listener seats using the drawing toolset of the CAD editor
- Specifically, listener seats can also be inserted on faces and on audience areas and will be automatically placed at ear height
- A preview shows the seat symbol at the listener position in advance
The primary properties of a listener seat are configured through its properties window.
- User-defined label
- Position (X, Y, Z coordinates)
- Orientation (Hor, Ver, Rot angles)
- Grouping and tables
-
Grouping and tables
- Multi-select of room items is available for all modification functions
- Loudspeakers can be assigned to processing blocks according to necessary signal processing
- Faces can be grouped by their materials
- Selection sets can be used to group any selection of items and recall them for viewing and modification
Selection sets
- Create, modify and delete sets of selected items with user-defined names
- Cross-highlight included items in other windows and vice versa
- View properties of included items such as assigned speaker models and acoustic materials
- Recall selection for all room modification functions and calculations
- Select all items of one type such as all loudspeakers or all faces
- Select single items and subsets of items for further use
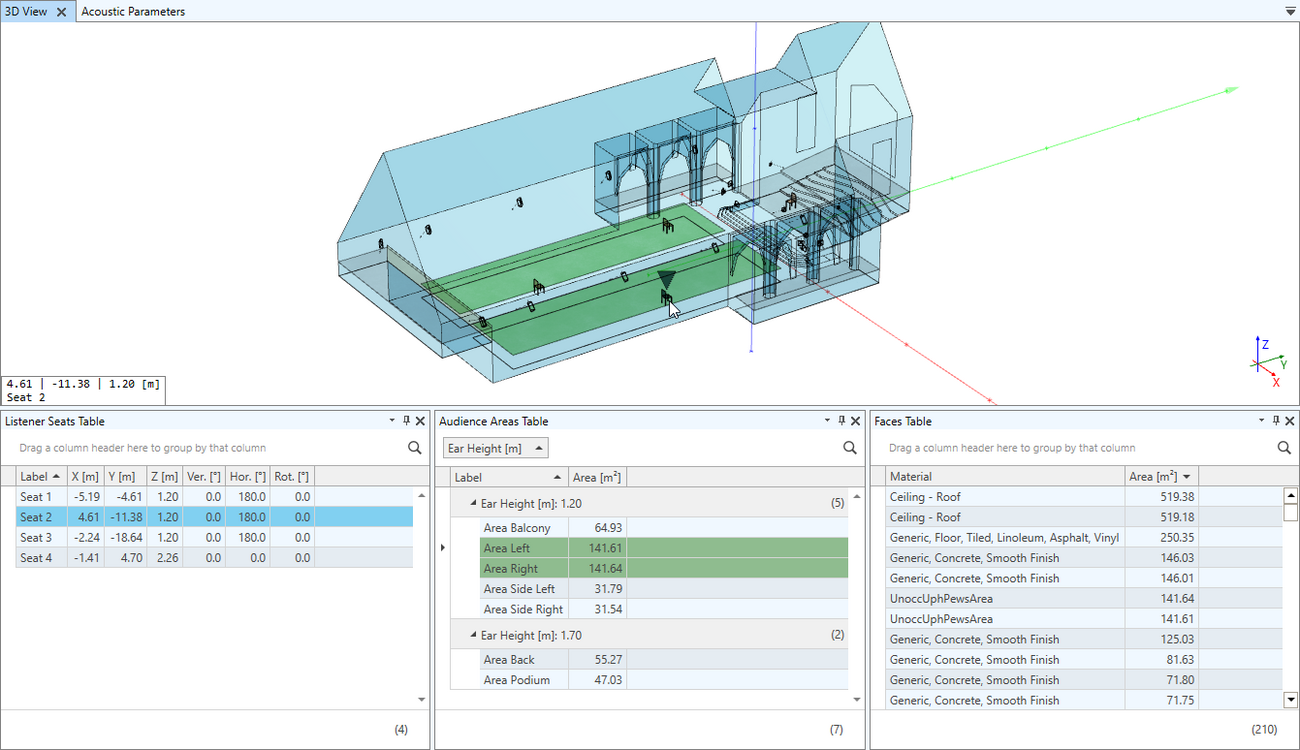
Interactive table functions- Room items can be viewed, highlighted and selected in tables
- Tables can be sorted, searched, and grouped
- User-defined layout including arrangement of columns
- Detailed filtering functions and customizable table summary
- Available for faces, loudspeakers, audience areas, listener seats and materials
- Calculation parameters
-
Calculation parameters
- Supported frequency range: Acousteer real-time mapping, material absorption curves and project parameters from 25 Hz to 20 kHz, room-acoustic calculation results from 100 Hz to 10 kHz
- Calculation in bandwidths of 1/3rd octave, 1/1 octave, 3 octave, broadband or user-defined, Acousteer real-time mapping also 1/24 octave (Std, Pro)
- SPL can be viewed Z-weighted and A-weighted, Acousteer real-time mapping also C-weighted
- Power summation and complex summation options
- Supported input signals: Pink noise, speech for STI applications (IEC 60268-16:2020), speech for office environments (ISO 3382-3), music (EIA 426B), program (IEC 60268-1)
- Apply changes to signal level and noise level after mapping calculations and update STI results without recalculation (Std, Pro)
- Automatic STI optimization function for determining best signal level at given S/N (Std, Pro)
- Direct field mapping (JR, Std, Pro)
-
The direct field mapping functions of EASE 5 offer a set of different result outputs that are used to optimize the setup of the sound system.
The Acousteer real-time mappings for Direct SPL coverage and Arrival Time distribution are available directly from the main program of EASE 5. These are fully integrated with all model parameters.
Image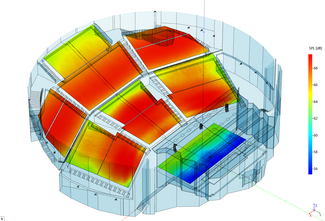
The Room Mapping module provides the mapping results in a conventional way.
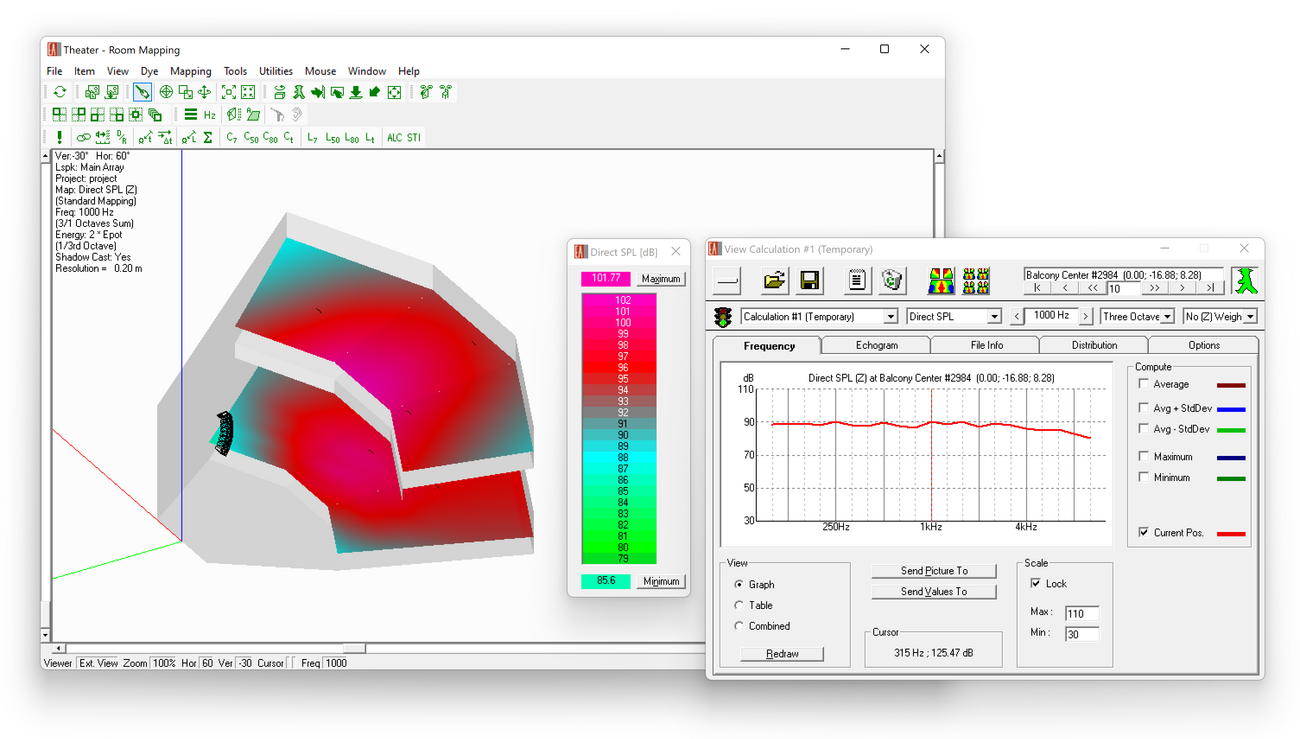
The conventional direct field mapping results include the following mappings:
- Direct SPL
- Arrival times
- Loudspeaker coverage overlap
- Initial Time Delay (ITD) Gap
- Loudspeaker density (3 dB, 6 dB, 10 dB)
- Horizontal angle of direction of localized source
- Mapping functions (JR, Std, Pro)
-
Acousteer real-time mappings can be calculated on audience areas and include the following functions:
- Interactive, live results without waiting time
- Continuous as well as isoline plots
- Peek Value mouse mode for reading results at user-defined locations
- Distribution statistics including spatial average, standard deviation, minimum and maximum values
- Adjustable legend colors and isoline steps
- Exporting pictures to file or clipboard
- Labeling, saving and loading calculation parameters and mapping results using simulation configurations
Conventional mappings can be calculated on faces, audience areas and listener seats and offer the following functions:
- Saving and opening mapping files
- Continuous as well as isoline plots on audience areas and faces
- Peek and Print Value mouse modes for reading results at user-defined locations
- Distribution statistics including spatial average, standard deviation, minimum and maximum values
- Cumulative distribution showing threshold and mean values for top 80%, 85%, 90% and 95% (e.g., for EN 54-32)
- Graphs showing corresponding frequency response curves
- Adjustable legend colors and isoline steps
- Result data can be exported in both text and graphic formats
- Statistical room acoustics (JR, Std, Pro)
-
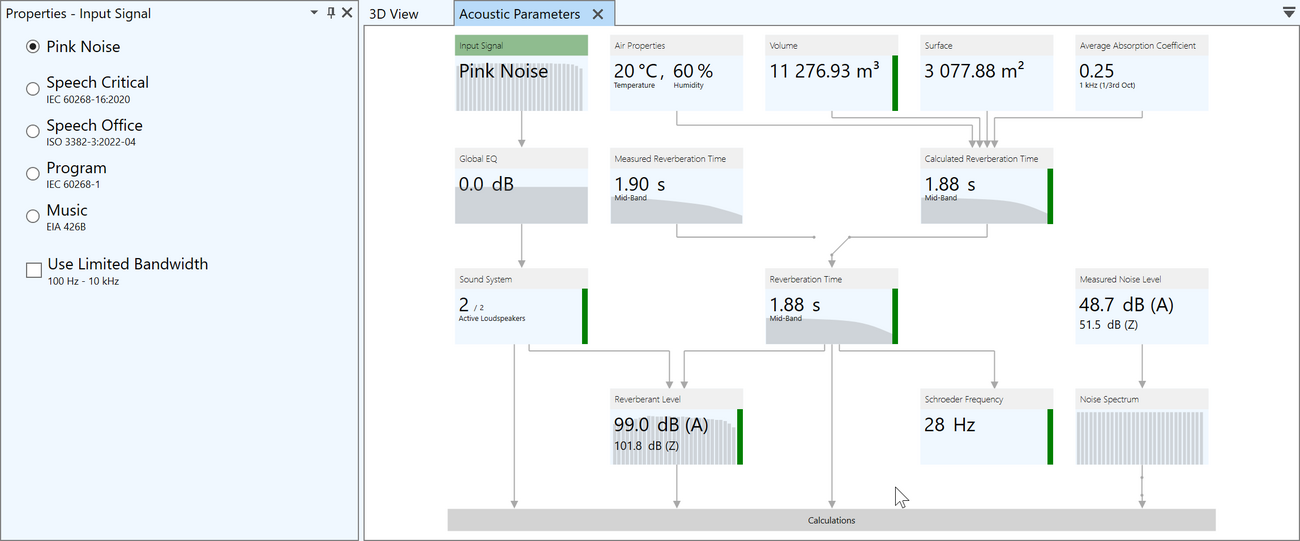
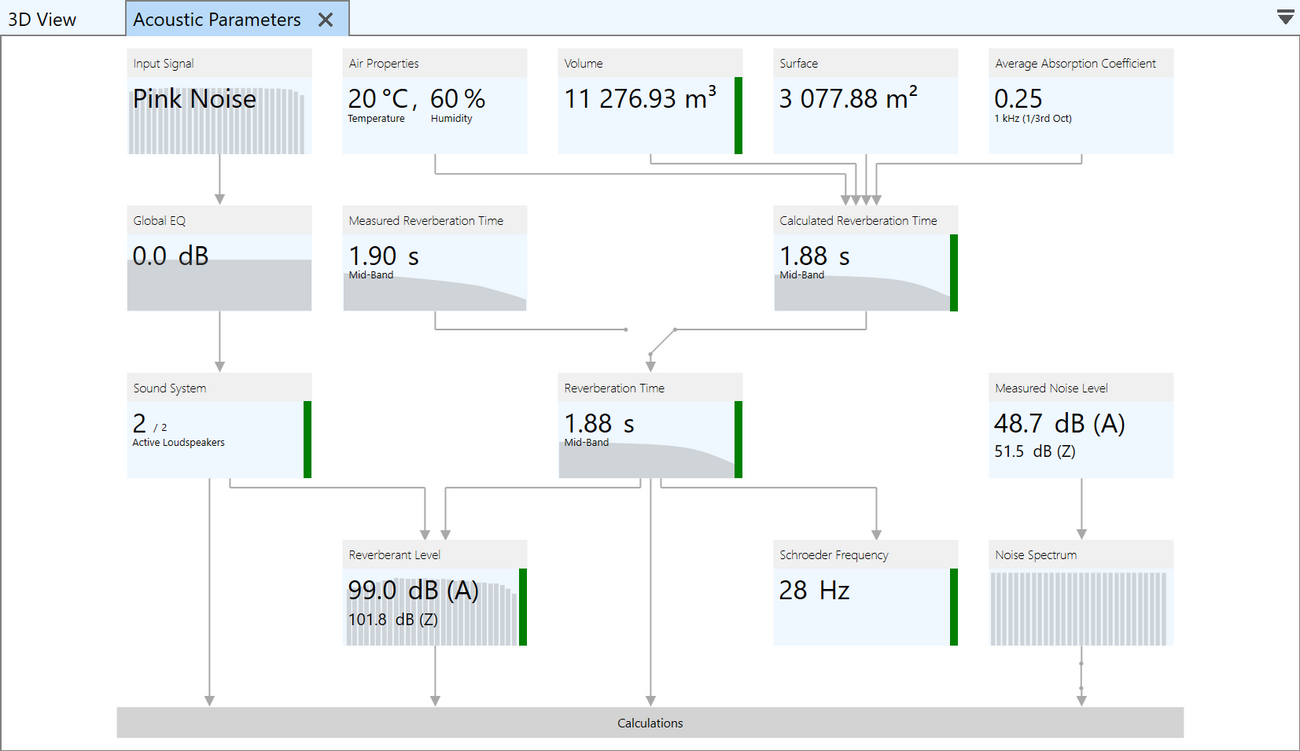
Acoustic parameters
In EASE 5, the main program provides an overview of all parameters needed for acoustic calculations in one view. These are used also for subsequent calculation and analyses.
- Air properties: temperature, pressure and humidity
- Volume - with indication for closed and open rooms.
- Surface area
- Average absorption coefficient
- Measured and calculated reverberation time (Eyring, Sabine)
- Assumed or measured noise level and noise spectrum
- Reverberant level
- Schroeder frequency
- Input signal, global EQ and sound system configuration
Input values can be modified easily, dependent results are immediately updated and visualized.
Mapping of room acoustic results
The mapping functions in EASE allow for a large number of simulations to be performed based on the diffuse-field assumptions of statistical acoustics. They employ the Eyring formula to compute the reverberation time which will be used to calculate acoustical parameters, such as STI (Speech Transmission Index) and Total SPL. Measured RT data can also be used for this type of mapping.
The Acousteer real-time mappings for Total SPL, D/R Ratio, Critical Distance and Signal-to-Noise Ratio are available directly from the main program of EASE 5. These are fully integrated with all model parameters.
Image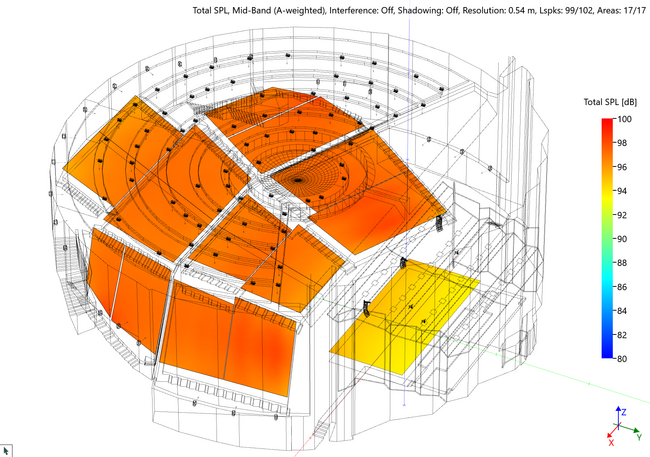
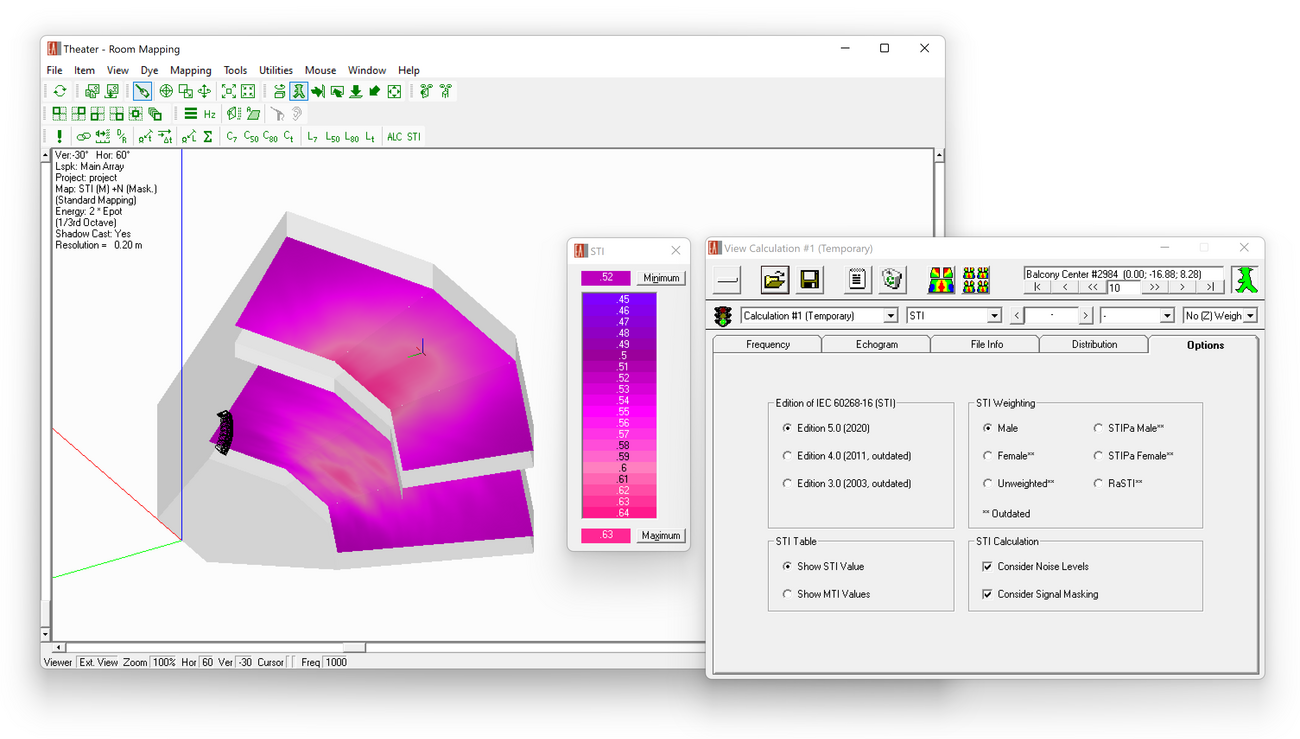
The Room Mapping module provides the mapping results in a conventional way via the Standard Mapping menu command.
In addition to the direct field results the following room acoustic results are provided using Standard Mapping functions:
- Total SPL – Sum of direct + reverberant sound field
- Speech intelligibility measures: STI according to IEC 60268-16:2020, RaSTI, ALCons
- D/R Ratio (Direct/Reverberant ratio)
- Critical Distance
- Clarity and Definition Measures: C7, C50, C80, C-Split
- Sound Pressure Levels: L7, L50, L80, L-Split
- Privacy Index, Articulation Index
- S/N Ratio
The same evaluation functions as for the direct field mapping are available for these mappings, as well.
- Ray-tracing and reflection analysis (Std, Pro)
-
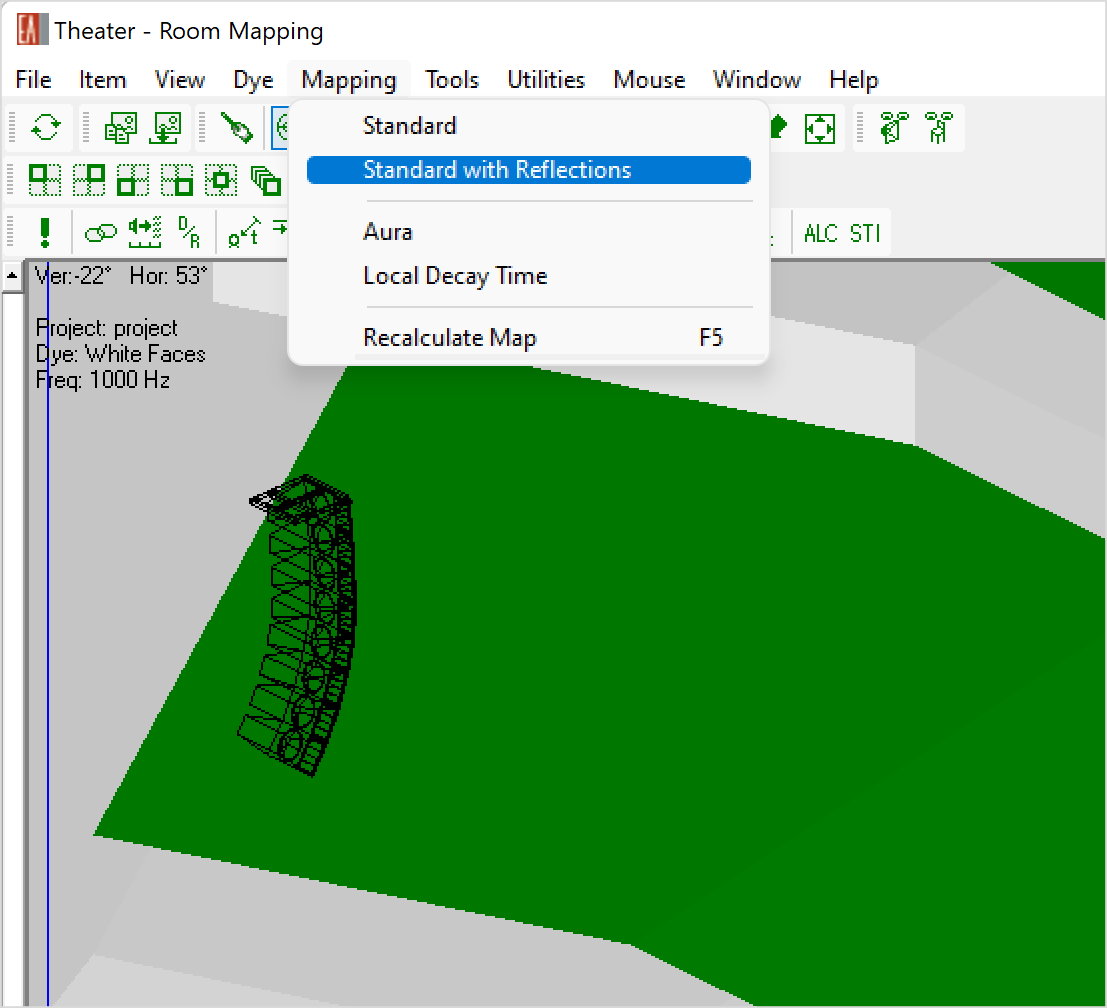
Standard Mapping with Reflections, Local Decay Time
Standard mapping results based on statistical acoustics can be extended by including early, specular reflections using simple ray-tracing functions. Using this combination, the same room acoustic quantities are calculated in a mapping format.
- Total SPL – Sum of direct + reverberant sound field
- Speech intelligibility measures: STI according to IEC 60268-16:2020, RaSTI, ALCons
- D/R Ratio (Direct/Reverberant ratio)
- Critical Distance Clarity and Definition Measures: C7, C50, C80, C-Split
- Sound Pressure Levels: L7, L50, L80, L-Split
- Privacy Index, Articulation Index
- S/N Ratio
Additionally, the Local Decay Time mapping allow analyzing local reverberation times with respect to selected positions in the room.
The same evaluation functions as for the direct field mapping are available for these mappings, as well.
Reflection patterns
Using the Ray Tracing module, reflection patterns can be calculated, analyzed, and visualized in order to find, e.g., audible reflections, focusing effects, and flutter echoes. They can also be used to aim loudspeakers and reflectors. The following functions are available for this purpose:
- Control ray tracing process by cut-off criteria (reflection order, time) as well as number of rays
- Select loudspeakers of interest as ray sources
- Optionally, select faces that should be considered for reflections
- View results in the 3D model as rays or as sound particles, at fixed points for time or animated
- Color coding for different conditions and parameters
- Save and recall result files
Reflection analysis
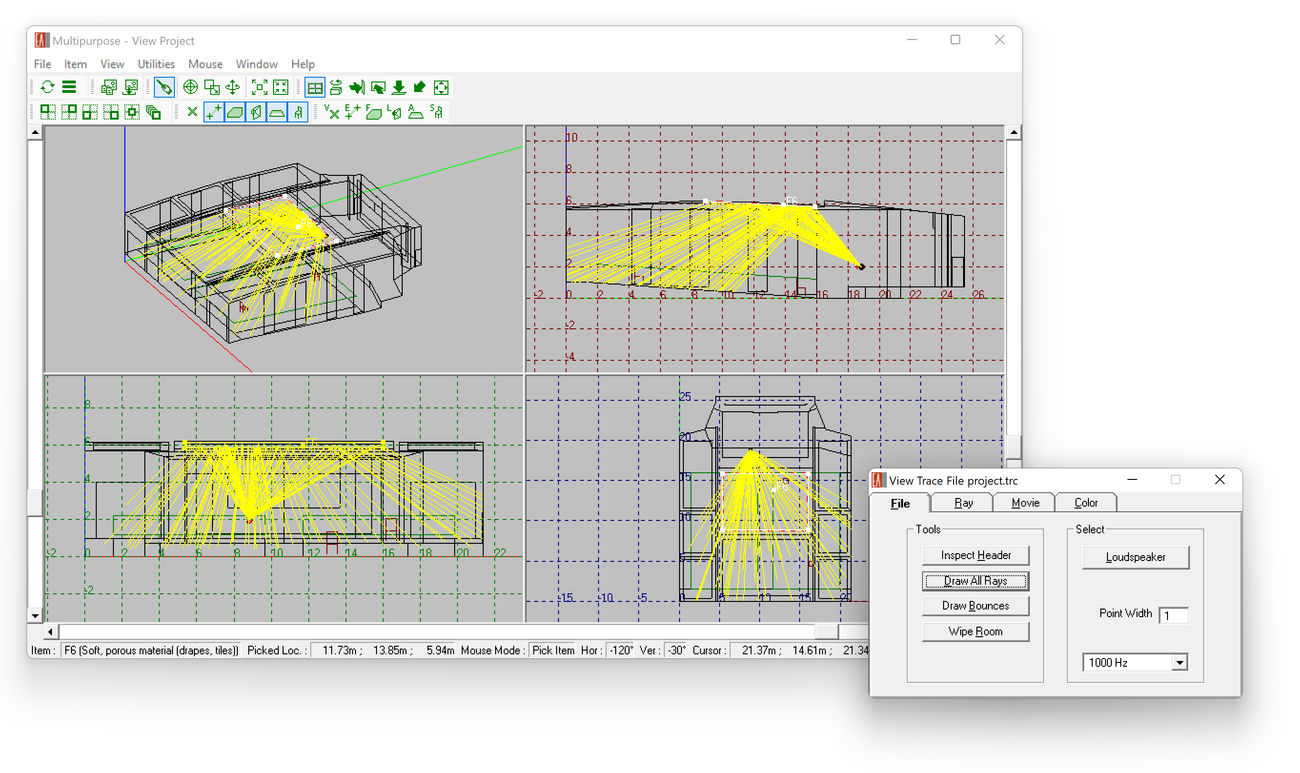
The Ray Tracing module also calculates response functions for user-defined locations in the room. These so-called reflectograms contain precise information about each reflection, such as its arrival time, level, frequency response, and direction given a listener seat or measurement position.
In combination with the Probe module and the 3D wireframe view of the Ray Tracing module, the reflectograms can be analyzed interactively in many different ways:
- Step through all reflections found and highlight each one in the 3D view and in the Probe reflectogram
- Select individual reflections in the Probe reflectogram view to identify and investigate the paths of audible echoes
- Use the Movie function to view an animation of sound particles moving through the room in 3D
- Use the 3D hedgehog display to obtain an impression which directions important reflections come from
- Look at reflection points and level losses along the propagation path of the ray
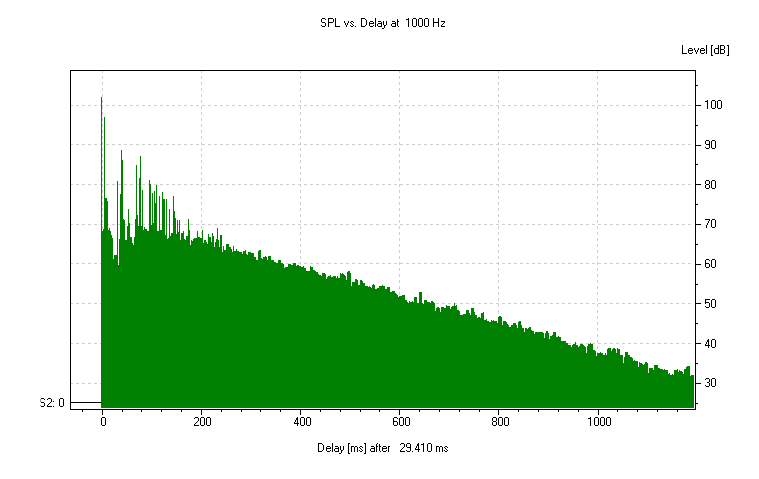
Measurement Probe
The Probe module of EASE 5 is used to view and analyze response files and reflectograms calculated primarily using ray-tracing methods. It works similar to a measurement suite and offers many different views and evaluation methods.
A number of displays are available, including:
- Reflectogram
- Impulse Response (IR) and Energy Time Curve (ETC)
- Waterfall
- Frequency Response (for sound sources and even for each reflection)
- Sound Pressure Levels (Direct SPL, L7, L50, L80, Total SPL, L-Split)
- 3D Hedgehog (Direction and Relative Level – Horizontal, Vertical or 3D)
- Phase Angles
- Reverberation Times including Schroeder RT, Eyring RT and tolerance ranges
- Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Speech Transmission Index (STI) according to IEC 60268-16:2020
- Clarity and Definition Measures (C7, C50, C80)
If the response is not the result of a full-length ray tracing simulation using AURA, it can be extended by a predicted tail to obtain an approximately complete impulse response.
Further editing and analysis functions include the ability of activating or deactivating parts of the response:
- Loudspeakers
- Reflection orders
- Single reflections
The response file can be transferred to the EARS module for auralization (Pro feature level only).
- Full-length mapping and response analysis (Pro)
-
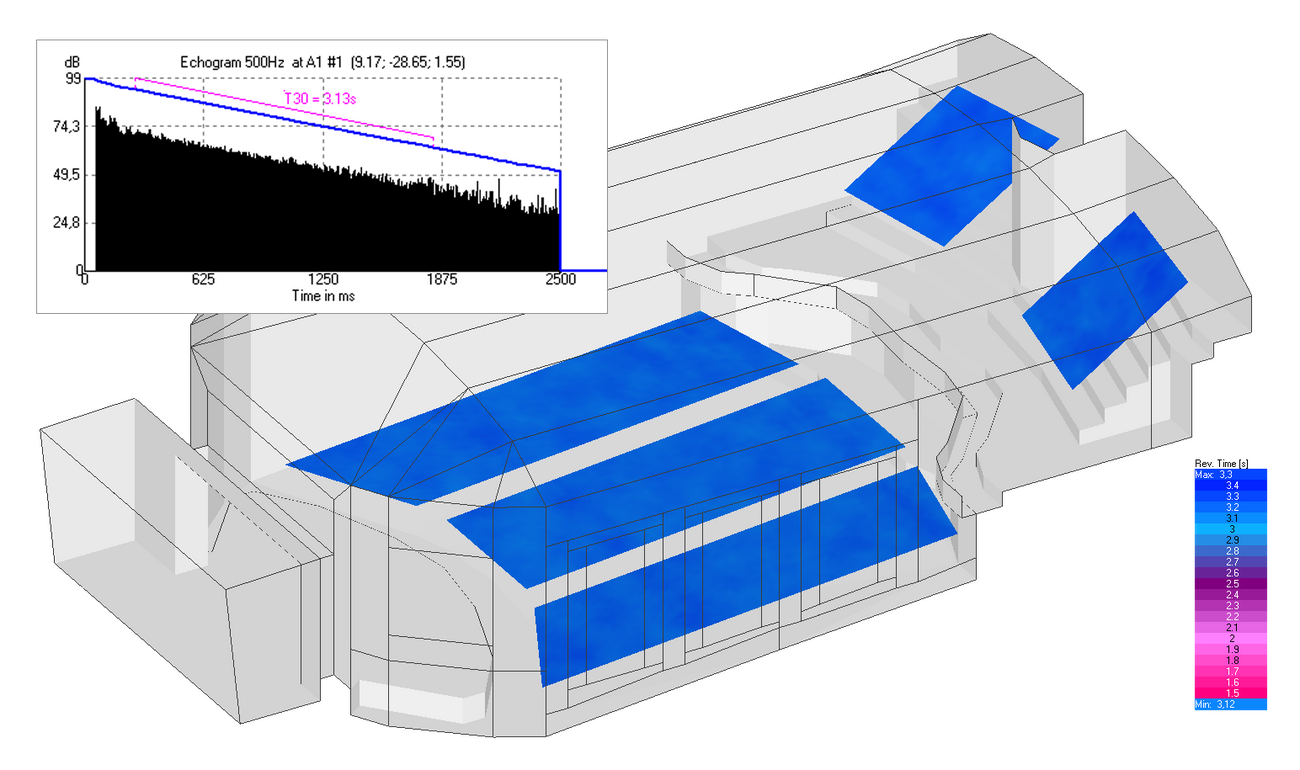
Full-length analysis with scattering (AURA module)
The AURA module provides advanced ray-tracing functions. They make use of a 64-bit engine and multi-threading in order to calculate accurate, full-length echograms and impulse responses including scattering effects and without tail estimates. This allows deriving all important acoustic quantities according to ISO 3382 and IEC 60268-16 with high accuracy.
Important calculation parameters for calculating full-length mappings and room responses can be adjusted by the user, including:
- Time length (cut-off time)
- Number of particles
- Scattering curve including the so-called S-curve
- Number of threads
- Loudspeakers in use
Image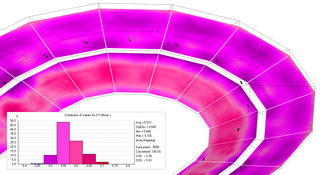
Full-length mapping
The AURA Mapping function provides the following results in a mapping format:
- Direct SPL
- Arrival Time
- Total SPL
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio
- Clarity and Definition Measures (D, C50, C80)
- Center Time
- Reverberation Times EDT, T10, T20, T30
- Lateral Fraction LF and LFC
- Sound Strength G
- STI (according to IEC 60268-16:2020) and ALCons
- Echo Criteria for Music and Speech
The same evaluation functions as for the direct field mapping are available for these mappings, as well.
For each receiver position the following data is additionally available:
- Echograms for all frequencies
- Histogram
- Integration curves for echo criteria
- Forward energy sum, Schroeder backward integral and intensity integral
Full-length response analysis
The AURA Response function calculates full-length response files in the following formats:
- Response (RSP) files for detailed analysis in Probe module
- Binaural (BIR) files for auralization in EARS module
- B-Format (WAV) files for auralization in Ambisonics setups
The same Probe evaluation functions as for specular ray-tracing results are available for AURA Response results.
- Full-length auralization (Pro)
-
Auralization is the process of simulating and making audible the effects of playing a known reference sound, such as program material, through a defined loudspeaker system in a particular space. It allows listening to the room before it is even built and therefore allows adding subjective impressions to the design process.
The EARS module of EASE 5 provides the means to perform auralizations. These can be based on the direct sound response only or on the results of specular ray-tracing runs with or without a predicted tail. However, the most accurate listening results are achieved using the output of AURA Response calculations.
Many different effects can be made audible using the EARS auralization module:
- Listener vs loudspeaker location and orientation
- Level differences and directions
- Localization of sources
- Colorations
- Flutter echoes
- Slap-back reflections
Image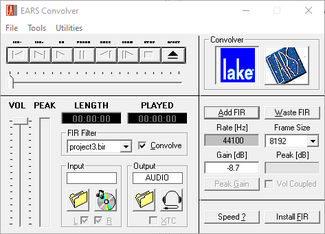
Additionally, the following main features are provided by the EARS module:
- Creation of BIR filter files using selected HRTFs
- Display of BIR files as binaural impulse response or frequency response
- Auralization using BIR files and dry signal input files (WAV) or from a live source (real-time convolution)
- Stereo convolution and mixing
- Built-in signal generator
- Batch processing for preparing multiple auralizations
Supported Brands
-
Supported Brands Table
- Loudspeaker Database